Introduction: Why the German Volume Training Plan Still Dominates Muscle-Building Strategies
When it comes to sculpting impressive muscle mass and enhancing strength efficiently, few programs rival the effectiveness of the German volume training plan. Revered by bodybuilders and strength athletes alike, this high-volume methodology has stood the test of time, offering a systematic and results-driven path to hypertrophy. Known for its trademark 10 sets of 10 reps structure, GVT is not for the faint-hearted—it demands unwavering discipline, careful programming, and deliberate execution. But those who commit to its rigors often walk away with dramatic gains in both size and muscular endurance.
Developed in the mid-20th century by German coaches and later popularized by strength guru Charles Poliquin, this program’s impact has transcended generations. Today, it remains a cornerstone in muscle-building strategies, delivering measurable results through consistent overload and efficient recovery. Whether you’re seeking to break through a plateau or build a solid foundation of size and strength, understanding how to implement the german volume training plan effectively could be the key to unlocking your next level of performance.
You may also like: The Ultimate Hypertrophy Workout Program for Building Strength and Size
The History and Principles Behind German Volume Training
German training first gained prominence in the 1970s when national weightlifting coaches in Germany utilized it to help athletes gain lean mass during the off-season. The program’s main goal was to induce hypertrophy by dramatically increasing training volume rather than load. This concept flew in the face of traditional strength routines, which emphasized lower volume and higher intensity. Instead, German volume training pursued muscular growth through sheer repetition and prolonged time under tension.
The simplicity of the program is deceptive. While it requires no advanced equipment or exotic movements, its effectiveness lies in its consistency and progressive overload. Performing 10 sets of 10 repetitions with a moderate load taxes the body’s ability to recover and adapt, stimulating both fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibers over the course of a workout. As a result, the body undergoes significant cellular stress, metabolic fatigue, and microtrauma—all of which contribute to muscular growth when paired with adequate recovery.
A defining characteristic of german volume training is its commitment to compound lifts. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and bent-over rows form the backbone of the program. These multi-joint movements recruit multiple muscle groups, amplifying hormonal response and enhancing overall efficiency. Because of its foundational nature, GVT training is accessible to intermediate and advanced lifters who are willing to focus intensely on technique and progression.
Core Mechanics of a Successful German Volume Training Plan
Designing an effective german volume training plan begins with selecting a limited number of compound lifts per workout. The key is to concentrate effort on one primary movement, such as the bench press for chest or the squat for legs, and perform it for 10 sets of 10 repetitions. This becomes the stimulus for hypertrophy, with secondary movements providing additional balance and assistance.
A typical volume training routine based on GVT principles is structured around a five-day split. One of the most popular configurations includes:
- Day 1: Chest and Back
- Day 2: Legs and Abs
- Day 3: Rest
- Day 4: Arms and Shoulders
- Day 5: Rest or Active Recovery
This structure ensures that each muscle group receives a high volume stimulus while allowing adequate recovery before the next session. Overtraining is a common pitfall in high-volume programs, so rest days must be honored with the same discipline as training days.
The load selected for 10×10 sets should be about 60% of your 1-rep max. At this intensity, most lifters can complete all sets with consistent technique and maintain time under tension. Rest intervals between sets typically range from 60 to 90 seconds. Any longer, and you reduce the metabolic stress central to GVT; any shorter, and you risk compromising form and recovery within the session.
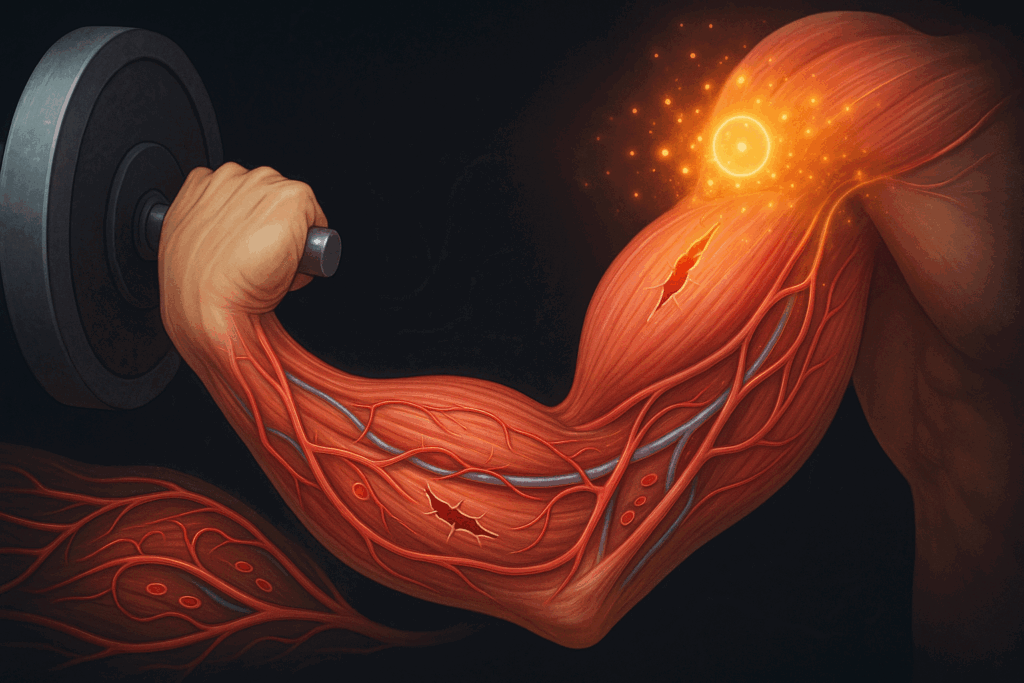
Physiology of Volume Training: Why It Works
The effectiveness of volume training programs like GVT lies in the body’s response to repeated stress. Muscle fibers adapt to tension by increasing in size, a process known as hypertrophy. With GVT, the high repetition count prolongs time under tension, particularly in the eccentric (lowering) phase of the lift. This creates micro-tears in the muscle fibers, which are repaired during recovery to form thicker, stronger tissue.
Beyond structural adaptation, GVT also enhances metabolic conditioning. Repeating 10 sets of an exercise increases lactic acid buildup, which in turn triggers the release of growth hormone—a critical agent in muscle repair and fat metabolism. Additionally, the sheer volume challenges the nervous system’s ability to maintain motor control and coordination, especially in later sets.
Another often overlooked benefit of german volume training is capillarization. The dense workload improves blood flow to muscle tissues by stimulating the development of new capillaries. This not only aids in nutrient delivery and waste removal but also enhances long-term recovery and work capacity.
Implementing the German Volume Training Plan for Optimal Hypertrophy
While GVT can be customized for various fitness goals, its most popular application is hypertrophy. To optimize your german volume training plan for muscle growth, you must focus on tempo control, nutrition, and program duration. Tempo refers to the speed at which you lift and lower the weight. A controlled 4-0-2-0 tempo (four seconds down, no pause, two seconds up, no pause at the top) maximizes time under tension and encourages more muscular activation.
Nutrition is equally critical. GVT burns through glycogen stores rapidly, necessitating a high carbohydrate intake to support energy and recovery. Protein requirements are also elevated, typically falling between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. This supports tissue repair and ongoing protein synthesis following the intense training loads.
As a high-stress protocol, GVT should be followed for no more than 4 to 6 weeks at a time. Beyond this period, the risk of overtraining increases, and progress often plateaus. Transitioning into a lower-volume or strength-based routine helps consolidate gains and prevent stagnation.

Modifying German Volume Training for Fat Loss and Athletic Conditioning
Although traditionally focused on hypertrophy, german volume training can be adapted for other goals, including fat loss and conditioning. For fat loss, one strategy involves pairing GVT sessions with metabolic finishers or high-intensity interval training. This combination elevates calorie expenditure and keeps the metabolism elevated post-workout.
Adjusting rest periods is another lever. Reducing the interval between sets to 45–60 seconds increases the cardiovascular demand, making each session more aerobically challenging. Additionally, incorporating circuit formats or supersets with non-competing movements—such as pairing squats with push-ups or deadlifts with planks—can maintain intensity without overloading a single muscle group.
Athletes aiming to improve sport-specific performance can use GVT principles selectively. For instance, instead of 10×10 squats, an athlete might perform 6×6 with explosive intent, integrating plyometrics or medicine ball throws in the accessory segment. This hybrid approach builds foundational strength while preserving agility, power, and neuromuscular speed.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in GVT Training
Many trainees are seduced by the simplicity of GVT but fail to respect its intensity. The most common mistake is choosing a weight that’s too heavy. While it may feel satisfying to lift near-maximal loads, this undermines the cumulative effect of high-volume work. The goal is to induce hypertrophy through repetition and time under tension, not through brute force.
Another pitfall is failing to follow tempo guidelines. Speeding through reps to “get it over with” diminishes mechanical tension and shifts the workload away from the intended muscle group. Each rep should be deliberate and controlled, especially during the eccentric phase.
Rest days are also critical. Overtraining symptoms—such as fatigue, irritability, and lack of progress—often appear when recovery is neglected. Given the demands of a volume training routine, active recovery strategies like light cardio, stretching, or foam rolling are invaluable for maintaining performance and reducing injury risk.
Fine-Tuning the Volume Training Routine for Long-Term Progress
Long-term success with any volume training program requires planned variation. After 4 to 6 weeks of traditional GVT, transitioning into another training block helps stimulate fresh adaptations. One option is to shift to a strength phase using lower reps (e.g., 5×5), focusing on heavier loads and longer rest periods.
Another strategy involves rotating exercises. Swapping back squats for front squats or switching from bench press to dips targets the same muscle groups from new angles, preventing stagnation and overuse injuries. Variability in accessory movements also keeps training mentally engaging and physically balanced.
Tracking performance metrics—such as completed reps, rest intervals, perceived exertion, and recovery quality—can provide early indicators of when to adjust. If strength continues to improve but hypertrophy slows, it may be time to revisit GVT with slight tweaks in volume or intensity.

Supporting Your German Volume Training Plan With Proper Nutrition
Fueling the body correctly is essential for success in gvt training. High-volume workouts demand an abundant supply of macronutrients, especially carbohydrates and protein. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source during resistance training, and without adequate intake, performance and recovery suffer.
To replenish glycogen stores and support recovery, aim for a carbohydrate intake of 4–6 grams per kilogram of body weight, particularly around workouts. Protein, on the other hand, should be consumed consistently throughout the day. Emphasize complete sources such as chicken, eggs, dairy, or plant-based protein blends to maximize muscle repair and growth.
Don’t overlook micronutrients and hydration. Magnesium, zinc, and B-complex vitamins play key roles in muscle function, energy metabolism, and hormonal health. Staying hydrated improves circulation and waste removal—both vital during recovery from a high-volume training session.

Recovery Strategies That Maximize Gains from GVT Training
Because of its demanding nature, german volume training requires strategic recovery planning. Sleep is the foundation. Prioritize 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep per night, as this is when most muscle repair and hormonal regulation occurs. Inadequate sleep disrupts recovery and limits the benefits of training.
Massage, contrast baths, and stretching sessions help flush metabolic byproducts from muscle tissue, accelerating the healing process. Active recovery sessions—such as walking, cycling, or swimming—enhance circulation without adding additional stress to the musculoskeletal system.
Mental recovery matters too. High-volume programs are psychologically demanding, so mindfulness practices, journaling, or even listening to music can support stress management. Lowering mental fatigue often improves physical output, especially over long training cycles.

Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments for Continued Growth
No matter how well-structured your volume training routine is, results plateau without regular reassessment. Keeping a detailed log of your sessions—including weights used, number of reps completed, and rest intervals—provides the feedback needed to adapt and improve.
Once all 10 sets of 10 reps are completed at a given weight with consistent form, increase the load slightly in your next session. If you’re struggling to hit target reps in the final sets, consider adjusting the rest interval or reviewing your nutrition and sleep.
Listening to your body is essential. If soreness becomes chronic or enthusiasm wanes, it may be time for a deload week or a temporary switch in training style. Training longevity hinges on avoiding burnout while preserving progression.
Frequently Asked Questions About German Volume Training
How does the german volume training plan affect mental resilience and discipline?
While the german volume training plan is renowned for its physical demands, its impact on psychological conditioning is equally significant. The mental challenge of completing 10 grueling sets of a single exercise cultivates a high level of focus, perseverance, and pain tolerance. Athletes often report improved confidence and grit in other areas of life after completing several weeks of consistent GVT training. The monotony of repeating the same movement for so many sets can test one’s patience, requiring deep commitment and a clear purpose. Over time, sticking to a volume training routine like GVT instills a mental toughness that benefits both training and broader life endeavors, reinforcing the link between discipline and results.
Can the german volume training plan be adapted for older adults or those returning from injury?
Yes, the german volume training plan can be modified for older adults or those recovering from injury, though with careful adjustments. Reducing the volume to 6 or 8 sets and incorporating more joint-friendly movements can preserve the hypertrophy stimulus without compromising safety. Machines or cable-based exercises may replace barbell lifts to minimize strain on joints. It’s also crucial to allow longer rest intervals and to use a slightly lower load to accommodate slower recovery capacities. When combined with physical therapy principles and close monitoring, a lower-intensity version of GVT training can still support muscle maintenance and functional strength for aging populations or post-injury rehabilitation.
What role does exercise order play in optimizing german volume training?
Exercise order is an underappreciated factor in maximizing the results of a german volume training plan. Starting with a multi-joint compound lift ensures that the most neurologically and metabolically taxing movement is performed when the body is freshest. Subsequent isolation or assistance exercises are then better able to target specific muscles without risking systemic fatigue. For instance, pairing squats with leg curls or bench presses with triceps extensions allows for comprehensive development without compromising primary lift quality. Changing the order periodically can also help overcome plateaus by altering the recruitment pattern and stimulus, a subtle but effective strategy within any well-designed volume training program.
How do different body types respond to german volume training?
Body types, or somatotypes, can influence how individuals respond to GVT training. Ectomorphs, who naturally have a leaner build, may find the volume helpful for adding size, but they must consume significantly more calories to support recovery. Mesomorphs, often predisposed to muscularity, typically see rapid results from a structured volume training routine due to their high responsiveness to hypertrophy protocols. Endomorphs may gain muscle quickly as well but should be mindful of dietary intake to avoid excessive fat accumulation. Regardless of body type, customization—particularly in terms of frequency, rest, and nutritional support—is key to optimizing results with any german volume training plan.
Are there any advanced periodization strategies compatible with GVT training?
Absolutely. While traditional GVT follows a linear progression model, integrating periodization can enhance long-term progress and prevent overtraining. One effective method is undulating periodization, which varies the volume and intensity across different weeks or sessions. For example, alternating between 10×10 and 5×5 schemes on different training days can stimulate both hypertrophy and strength adaptations. Another option is block periodization, where GVT is used during a hypertrophy block, followed by a strength or power phase to consolidate gains. These strategies ensure the central nervous system remains challenged while allowing adequate recovery between training blocks, maximizing the benefits of a high-volume training routine.
How does sleep specifically influence results from the german volume training plan?
Sleep is a crucial, often underestimated component in the success of any german volume training plan. During deep sleep cycles, the body releases growth hormone, which facilitates tissue repair and muscle recovery. Inadequate sleep not only impairs this hormonal process but also diminishes neuromuscular coordination and training performance. Chronic sleep deficits can blunt the anabolic response to resistance training, limiting the effectiveness of high-volume programs like GVT training. Athletes following a demanding volume training routine should prioritize 7–9 hours of uninterrupted sleep, and consider short daytime naps during particularly intense training phases for enhanced recovery.
How can technology and fitness tracking tools enhance GVT performance?
Modern technology offers tools that can significantly optimize execution of the german volume training plan. Wearable devices can monitor heart rate variability (HRV), an important indicator of recovery and readiness for high-volume training. Apps that track set completion time, rest periods, and tempo ensure consistency and allow for data-driven adjustments. Some advanced platforms even analyze lifting velocity, helping lifters maintain power output across all 10 sets. For those managing a long-term volume training routine, digital tracking allows trends to emerge—revealing when to push, when to deload, and how different strategies affect results over time. This integration of tech into traditional training can elevate GVT’s already powerful effects.
What social or community dynamics support success with german training?
Group support and accountability can be instrumental in maintaining consistency with german training, which is often physically and mentally taxing. Training with a partner or within a structured gym community can provide encouragement during grueling sets and help enforce rest intervals. Some lifters benefit from sharing progress on fitness forums or social media, which can increase motivation and provide valuable feedback from more experienced trainees. Furthermore, being surrounded by others who value discipline and high performance can foster an environment where the german volume training plan becomes not just a routine but a shared challenge. This social component adds a motivational edge that complements the physiological demands of the program.
How can GVT training be integrated into sports-specific conditioning programs?
Incorporating gvt training into sport-specific conditioning requires careful balancing of volume, intensity, and specificity. For athletes in power-dependent sports like football or rugby, GVT can be used in the off-season to build base hypertrophy before transitioning to explosive training. In contrast, endurance athletes might use modified GVT protocols—fewer sets, lighter weights—to build muscular stamina without impairing mobility or speed. Exercise selection should reflect the movement patterns and energy demands of the sport; for example, using split squats instead of back squats for field athletes. Coaches must also monitor fatigue closely to ensure that GVT doesn’t compromise skill development or on-field performance during competitive seasons.
What are the emerging innovations in volume training that may evolve the german volume training plan?
Emerging trends in strength science and biofeedback are poised to refine and evolve the traditional german volume training plan. Variable resistance tools, such as bands or chains, are being used to adjust resistance curves, increasing intensity during specific movement phases. Blood flow restriction (BFR) training is also being explored in conjunction with high-repetition sets to amplify hypertrophy with lighter loads. Nutrient timing technologies, wearable recovery devices, and AI-driven coaching apps are further enhancing personalization and efficiency. These advancements offer exciting potential to update GVT without compromising its core principles, ensuring that this proven volume training program remains relevant in an ever-advancing fitness landscape.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of German Volume Training for Lasting Results
The german volume training plan is more than just a program—it’s a discipline, a challenge, and a proven pathway to substantial muscle growth and increased strength. While it demands consistency, patience, and precision, the rewards are equally substantial. GVT stands as a testament to the idea that intensity doesn’t always mean lifting heavier weights; sometimes, it means doing more with less, over and over again.
By understanding its principles, customizing it to your goals, and supporting it with proper nutrition and recovery, you can make the most of this timeless approach. Whether your aim is hypertrophy, fat loss, or general performance, gvt training delivers lasting results when implemented intelligently. It pushes you to your limits and teaches resilience, rewarding effort with visible progress and renewed confidence.
Ultimately, the power of german volume training lies not just in its structure, but in its ability to instill discipline, transform physiques, and elevate mental fortitude. Embrace it with commitment, and it can become the foundation for your most powerful transformation yet.
Further Reading:
How German Volume Training Can Add Muscle to Your Frame
What to Know About German Volume Training for Gaining Muscle





