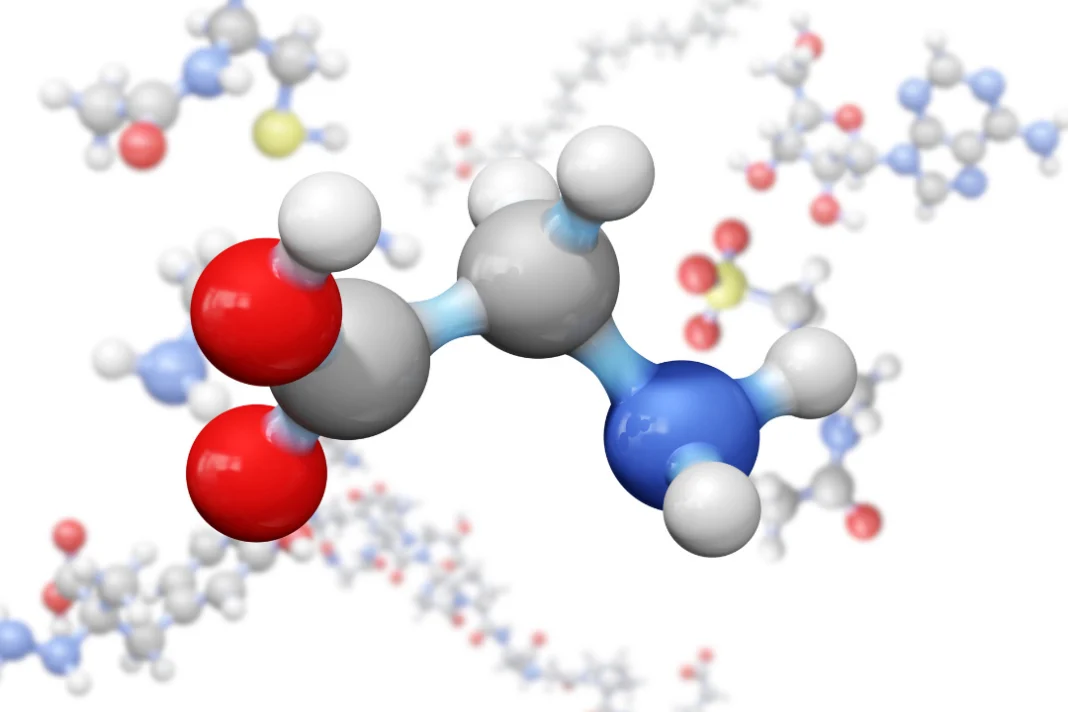
The body’s creation of proteins and cellular processes both depend on the amino acid glycine. Even though glycine can be produced by the body from other amino acids or compounds, however, its supplements may have positive effects on health, notably on cognition and general wellbeing. For people looking to improve focus and cognition, this article will give a thorough explanation of glycine, including its nature, health advantages, ideal dosage, side effects, potential drug interactions, and optimum responsible use.
Glycine (Collagen Amino Acid): Benefits, Dosage, Side Effects, Drug Interactions, And Other Important Information is an original (HisHealthMag) article.
Nature of Glycine
Glycine is the most basic amino acid and it is also known as the collagen amino acid because collagen contains high levels of glycine. Glycine functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain and is involved in the creation of proteins, DNA, and other significant biomolecules.

Health Benefits of Glycine
Studies on glycine’s possible health advantages, particularly in regard to cognitive function and general health, have been conducted. The following are a few reported health advantages of glycine:
1. Enhanced Cognitive Function: According to certain research, glycine may assist enhance cognition, memory, and attention. Those wanting to improve their mental performance for professional or academic goals may find this to be especially helpful.
2. Better Sleep: Studies have indicated that glycine may enhance sleep quality. It might shorten the time it takes to fall asleep and enhance the general quality of sleep, which would promote daytime alertness and cognitive function.
3. Glycine has been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation can lead to the development of a number of medical diseases. Therefore, reducing inflammation will lead to the overall health throughout the body.
4. Better Digestive Health: Glycine may also be advantageous for better digestion. It contributes to the bile acid synthesis necessary for the breakdown and absorption of dietary lipids.
Chemistry of Glycine (Collagen Amino Acid) and Physiological Mechanism of Action
Glycine has a very simple chemical structure with an amino and carboxyl side chain and a hydrogen atom as its R-group. It plays a role in the body’s creation of proteins, DNA, and other significant macromolecules. Moreover, glycine functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain, controlling synaptic transmission and modifying the excitability of neurons.
The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine receptors are two examples of particular receptors in the brain and nervous system where glycine binds to exert its effects. These receptors control how neurons behave and how we learn and remember. Glycine may enhance cognition, memory, and attention by regulating the activation of various receptors.
Glycine has also been demonstrated to have potential advantages for better sleep. It functions as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which helps to lower brain neuron activity and encourage relaxation. People will take a shorter time to fall asleep and this enhances the general quality of sleep.
Optimal Dosage of Glycine
The best amount of glycine to take depends on the needs and health of the individual. When taken in the recommended dosages, it is typically regarded as safe and well-tolerated. Typically, 1 to 3 grams of glycine per day are advised for optimal cognitive performance and restful sleep.

Side Effects of Glycine
When administered in the proper doses, glycine is generally regarded as safe and well-tolerated. High doses, however, could result in diarrhea, upset stomach, and nausea. It’s crucial to take the medication as directed and to speak with your doctor if you have any questions.
Potential Substance Interactions with Glycine
Glycine may interact with certain drugs and supplements. Here are a few instances of possible drug interactions with glycine:
- Antipsychotic drugs: Glycine may interact with antipsychotic drugs like risperidone and clozapine. It might make these drugs more strong, which could have unfavorable side effects.
- Blood thinners: Glycine and blood thinners like warfarin may interact. It could result in adverse side effects and raise the risk of bleeding.
3. Anti-anxiety drugs: Glycine and anti-anxiety drugs like benzodiazepines may interact. It might intensify the sedative effects of these drugs, which might result in unfavorable side effects.
Best Responsible Use of Glycine
It’s crucial to use a high-quality product from a respected supplier when thinking about using glycine. Glycine is a fantastic source in myPEAK Radiance, which is also designed to work well with other nootropics and be extremely bioavailable. While taking glycine as a supplement, it’s crucial to adhere to the advised dosage and speak with a doctor if you have any questions, especially if you take any drugs or already have a medical problem.
Glycine: Conclusion
Glycine is the most fundamental amino acid because it is the most prevalent and participates in the majority of metabolic reactions. Glycine may be favorable for your overall health, sleep quality, and cognitive performance. When thinking about taking glycine as a supplement, it’s crucial to use a high-quality product from a reliable supplier. MyPEAK Radiance Glycine supplements provide a great complement to other supplements, and they are extremely bioavailable. When administered in the proper dosage, it is typically regarded as safe and well-tolerated. However, advice and consultation from a certified healthcare provider are essential to ensure that the glycine supplement is suitable for you and will lead to an overall improvement in general health.
Important Note: The information contained in this article is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.