Building muscle is as much about smart eating as it is about intense training. When paired with a consistent resistance training regimen, expert-approved bulking meals can be the difference between lean muscle gains and unwanted fat accumulation. Bulking meals play a vital role in supporting your bulking diet by offering an optimal combination of macronutrients, especially high-quality proteins and energy-rich carbohydrates. For college graduates and fitness enthusiasts looking to advance their gains, understanding what to eat and when to eat it is essential for maximizing results.
You may also like : The Ultimate High-Protein Nutrition Plan: How to Gain Muscle in Women Safely and Effectively
Why Nutrition Matters in a Bulking Diet Plan
At its core, a bulking diet plan is built around creating a calorie surplus to stimulate muscle growth. But not all calories are created equal. The quality of the foods you consume directly affects your performance, recovery, and the quality of muscle mass you build. Protein supports muscle protein synthesis, carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores, and healthy fats regulate hormones crucial for growth. Without a well-structured bulking diet, even the most dedicated gym-goers may find themselves spinning their wheels.
Furthermore, a good bulking diet program takes into account not only the total caloric intake but also the timing and composition of meals. Eating the best bulking meals at strategic intervals throughout the day ensures your muscles are consistently nourished and primed for hypertrophy. Meal planning and prep become central elements in sustaining consistency and ensuring dietary adherence.
How to Structure the Perfect Bulking Meal Plan
Creating a successful bulking meal plan involves careful selection of nutrient-dense, whole foods that are rich in both calories and micronutrients. The best foods for bulking include lean meats, dairy products, whole grains, legumes, and a variety of fruits and vegetables. Each meal should contain a robust source of protein (at least 25 to 35 grams), a complex carbohydrate for sustained energy, and a moderate amount of healthy fats.
In practice, this could mean having a breakfast of oatmeal topped with almond butter and whey protein, a lunch featuring grilled salmon with quinoa and vegetables, and a dinner composed of turkey chili with beans and avocado. Snack times should not be overlooked; items like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese with fruit, and high-protein smoothies can keep the anabolic engine running throughout the day.
The success of a bulking meal plan also depends on sustainability. Meals should be easy to prepare, enjoyable to eat, and flexible enough to accommodate individual preferences. By rotating ingredients and experimenting with spices and cooking techniques, you can keep your bulking foods exciting and avoid burnout.
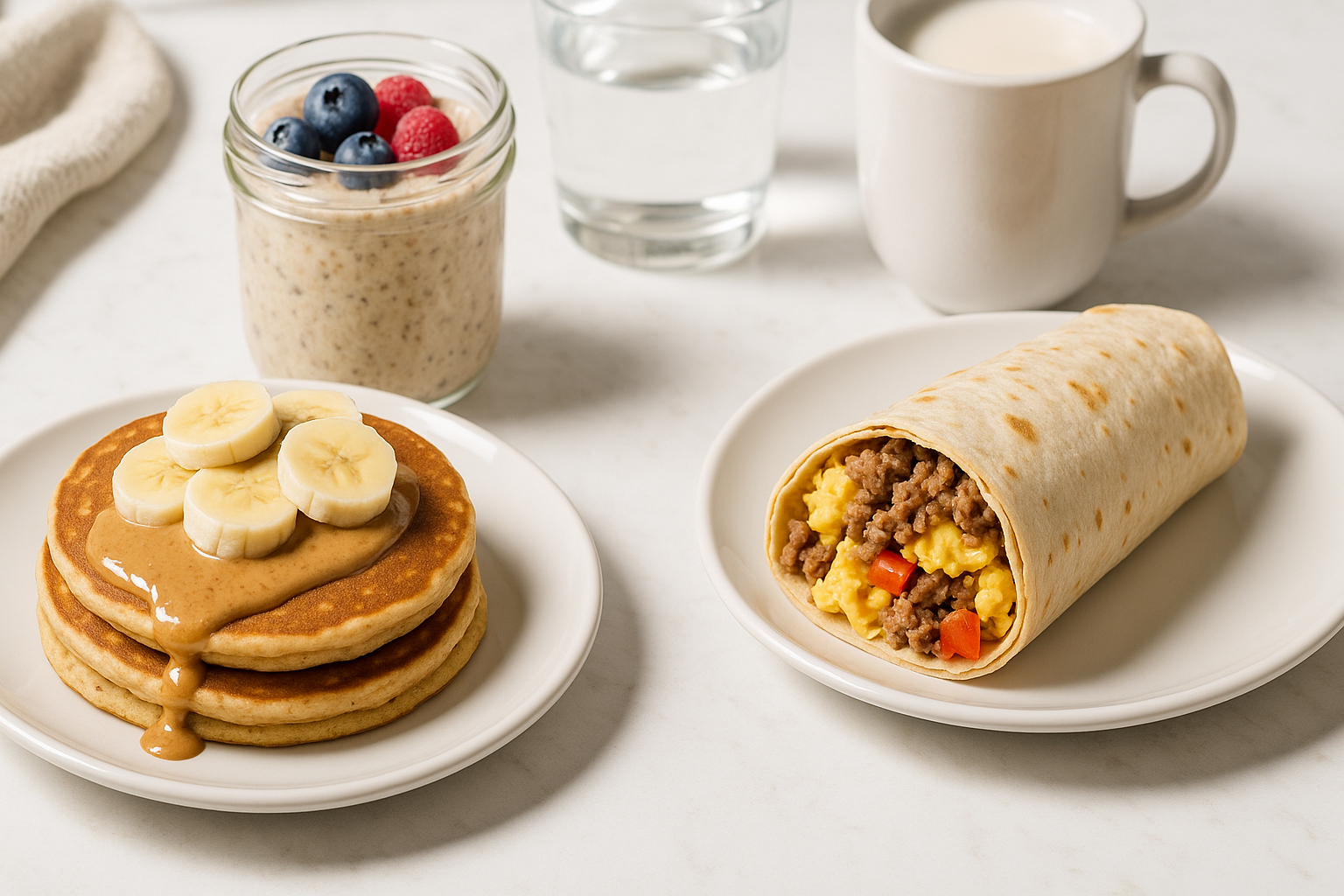

Top Breakfast Bulking Meals for Muscle Gains
The first meal of the day sets the stage for muscle recovery and performance. An effective bulking breakfast needs to balance energy, protein, and flavor to keep you satisfied and anabolic from the get-go. One classic example is a stack of protein pancakes made with oats, cottage cheese, eggs, and a scoop of protein powder. Topped with banana slices and a drizzle of almond butter, this meal hits every nutritional target.
Another powerful option is a hearty breakfast burrito loaded with scrambled eggs, lean ground beef, black beans, and cheese, all wrapped in a whole wheat tortilla. This meal provides not only protein but also a hefty dose of complex carbohydrates and fiber, making it ideal for fueling a morning workout or a demanding workday.
Overnight oats also make a convenient and highly customizable bulking breakfast. Mix rolled oats with Greek yogurt, chia seeds, and a scoop of protein powder, and let it sit overnight. In the morning, top it with berries, nuts, or even dark chocolate chips for a nutrient-dense and indulgent start to the day. These great bulking meals ensure you hit your macronutrient goals early and keep hunger at bay.
Mid-Morning Snacks That Support a Bulking Diet Program
Maintaining a consistent nutrient intake throughout the day is critical in any bulking diet. Mid-morning snacks help bridge the gap between breakfast and lunch while keeping your metabolism active and your muscles fed. One of the best bulking meals in snack form is a high-calorie smoothie made with whey protein, whole milk, oats, peanut butter, and a banana. It offers fast-digesting nutrients that are ideal post-workout or during a break.
Alternatively, a handful of trail mix made with mixed nuts, seeds, and dried fruits can serve as a compact, energy-dense snack. Add a few dark chocolate chunks for taste and antioxidants. Cottage cheese paired with pineapple or berries is another excellent snack, as it provides casein protein, which digests slowly and provides a sustained amino acid release.
Rice cakes with nut butter or whole-grain toast with avocado and eggs can also work well for those seeking more volume. These snacks support your bulking diet plan by contributing to your daily calorie goals without overwhelming your digestive system, thus maintaining energy and muscle-building momentum.
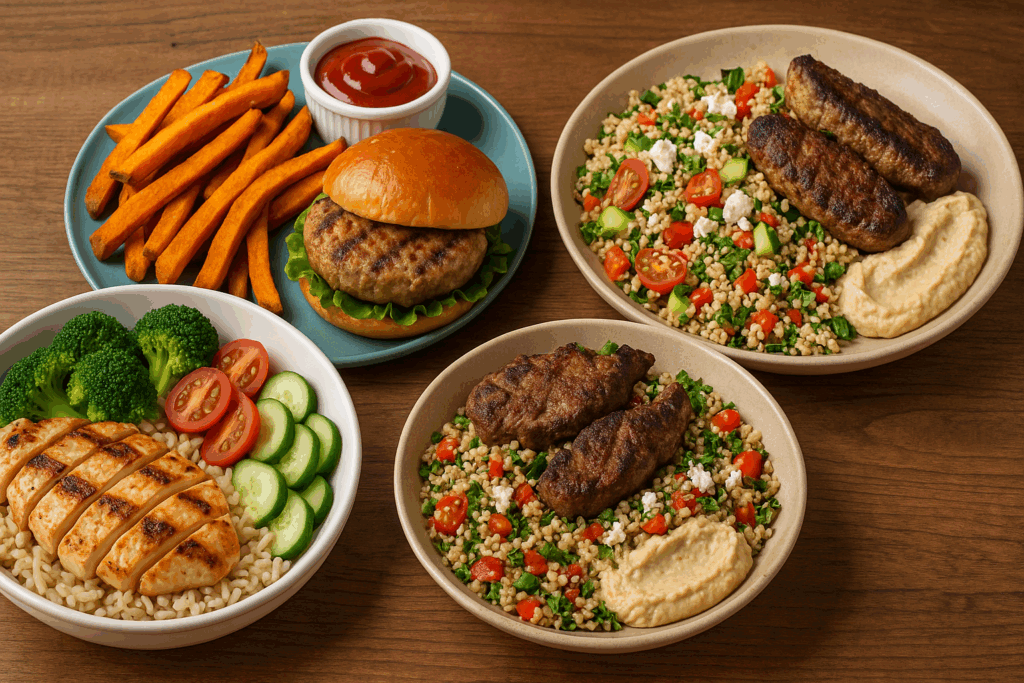
Bulking Meals for a Powerful Muscle-Building Lunch
Lunch is a prime opportunity to refuel your muscles and sustain anabolic activity. The best lunch options combine lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. A grilled chicken bowl with brown rice, roasted vegetables, and a tahini dressing provides a nutrient-rich meal that supports muscle growth and recovery.
Another reliable lunch is a turkey burger on a whole grain bun with sweet potato fries and a side of spinach salad. This meal balances flavor, satiety, and nutrient density. For those who enjoy Mediterranean flavors, a quinoa tabbouleh salad with grilled lamb or beef, olives, cucumbers, and hummus delivers on taste and bulking nutrition.
Stir-fries made with lean beef, tofu, or shrimp, paired with a colorful mix of vegetables and served over jasmine rice or whole-grain noodles, can be cooked in bulk and customized to fit any bulking meal plan. These meals are not only filling but also packed with diverse nutrients essential for cellular repair and protein synthesis.
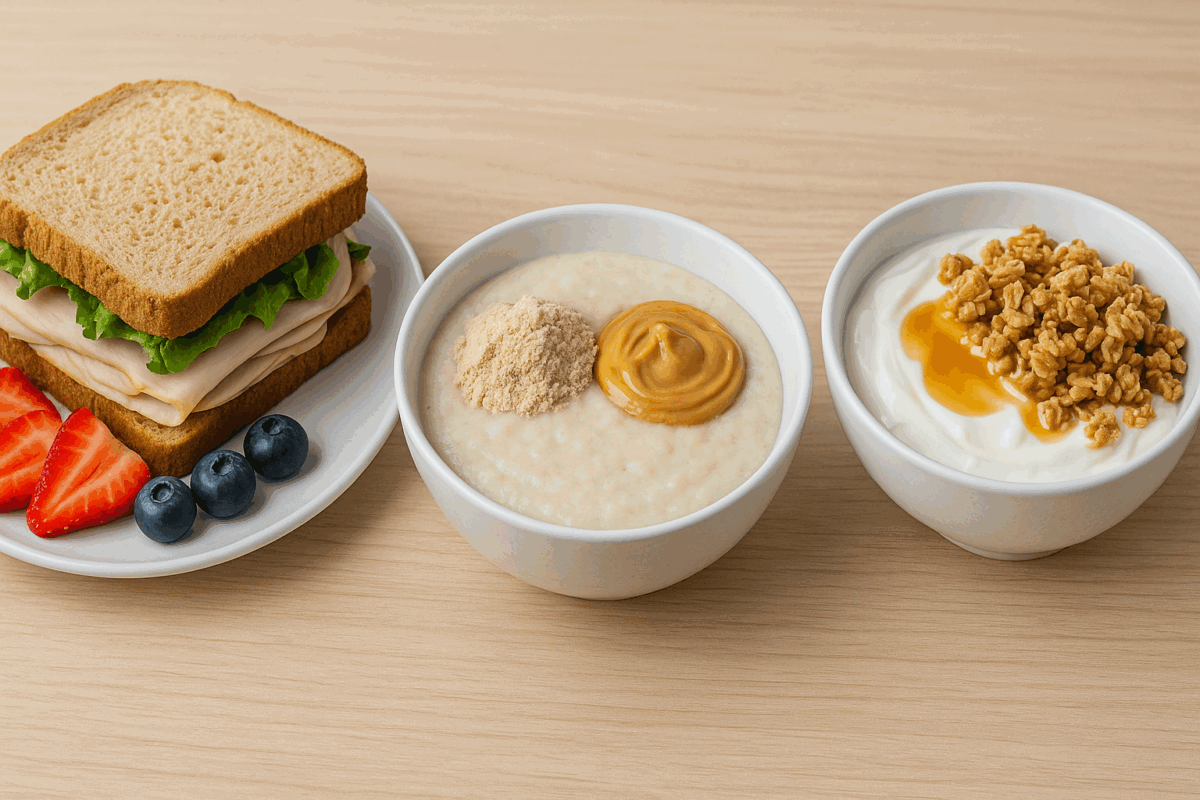
Smart Choices for Pre-Workout Bulking Foods
Pre-workout meals should focus on providing fuel without causing digestive discomfort. The goal is to consume a combination of protein and carbohydrates about 60 to 90 minutes before training. One smart option is a turkey and avocado sandwich on whole grain bread with a side of fruit. The complex carbs supply energy, while the protein supports muscle repair during and after the session.
Greek yogurt with honey and granola is another effective pre-workout meal. It’s light yet energy-dense, offering both quick and sustained release carbohydrates. Alternatively, a bowl of cream of rice with whey protein stirred in, plus a tablespoon of peanut butter for added calories and flavor, can make an ideal pre-training fuel source.
Choosing the right bulking foods before a workout ensures you train with maximum intensity, reduce the risk of muscle breakdown, and support a faster recovery window. These good foods for bulking not only enhance performance but also elevate your training outcomes.

Refueling With Post-Workout Bulking Meals for Maximum Recovery
After an intense workout, your body enters a recovery phase where it demands nutrients to repair and build muscle. Post-workout bulking meals should prioritize fast-digesting proteins and high-glycemic carbohydrates. A grilled chicken and white rice bowl with a fruit smoothie offers a simple yet effective combination for recovery.
Egg-white omelets with vegetables and toast can also make an excellent post-workout meal. Add a side of Greek yogurt or a whey protein shake to increase the protein content. Tuna and sweet potato mash is another winning combination, delivering both fast and slow-digesting carbs along with omega-3-rich protein.
The most effective bulking meal plan incorporates post-workout meals that are consumed within 30 to 60 minutes after training. Doing so maximizes muscle protein synthesis and glycogen replenishment, helping you recover faster and train harder in the following session.
Great Bulking Meals for Dinner and Evening Nutrition
Dinner provides a crucial opportunity to close your day with a nutrient-packed meal that supports overnight recovery. Lean meats such as grilled steak, turkey breast, or salmon served with quinoa, brown rice, or baked potatoes create a perfect end-of-day bulking plate. Add steamed vegetables and a drizzle of olive oil or avocado slices for fiber and healthy fats.
Hearty stews and chilis are also fantastic evening meals. Consider a slow-cooked beef and bean chili made with tomatoes, bell peppers, and garlic. These meals can be made in large batches, reheated easily, and offer high protein and calorie density, making them some of the best bulking meals for busy individuals.
Pasta dishes can also serve as powerful bulking meals when prepared correctly. Opt for whole grain or lentil pasta and add lean ground meat, vegetables, and a tomato-based sauce rich in herbs and spices. These satisfying dinners contribute significantly to your total daily intake and help repair and build muscle overnight.
The Psychological Impact of a Bulking Diet and How to Stay Consistent
Gaining weight—even as muscle—can be psychologically challenging for those accustomed to a leaner physique. The mental shift from restriction to surplus, and the temporary increase in body fat, may trigger self-doubt or body image concerns. It’s important to maintain perspective and remember that bulking is a strategic, temporary phase that serves a long-term goal.
Staying consistent requires motivation, but also mental resilience. Tracking progress through strength gains, measurements, and photos—not just the scale—can help you stay focused on what matters. Surrounding yourself with a supportive community, whether online or in person, reinforces accountability and shared purpose.
Reframing bulking meals as tools of empowerment rather than a source of anxiety allows you to maintain a healthy relationship with food. Remember, food is fuel, and building muscle is a form of self-respect that takes patience, strategy, and self-compassion.
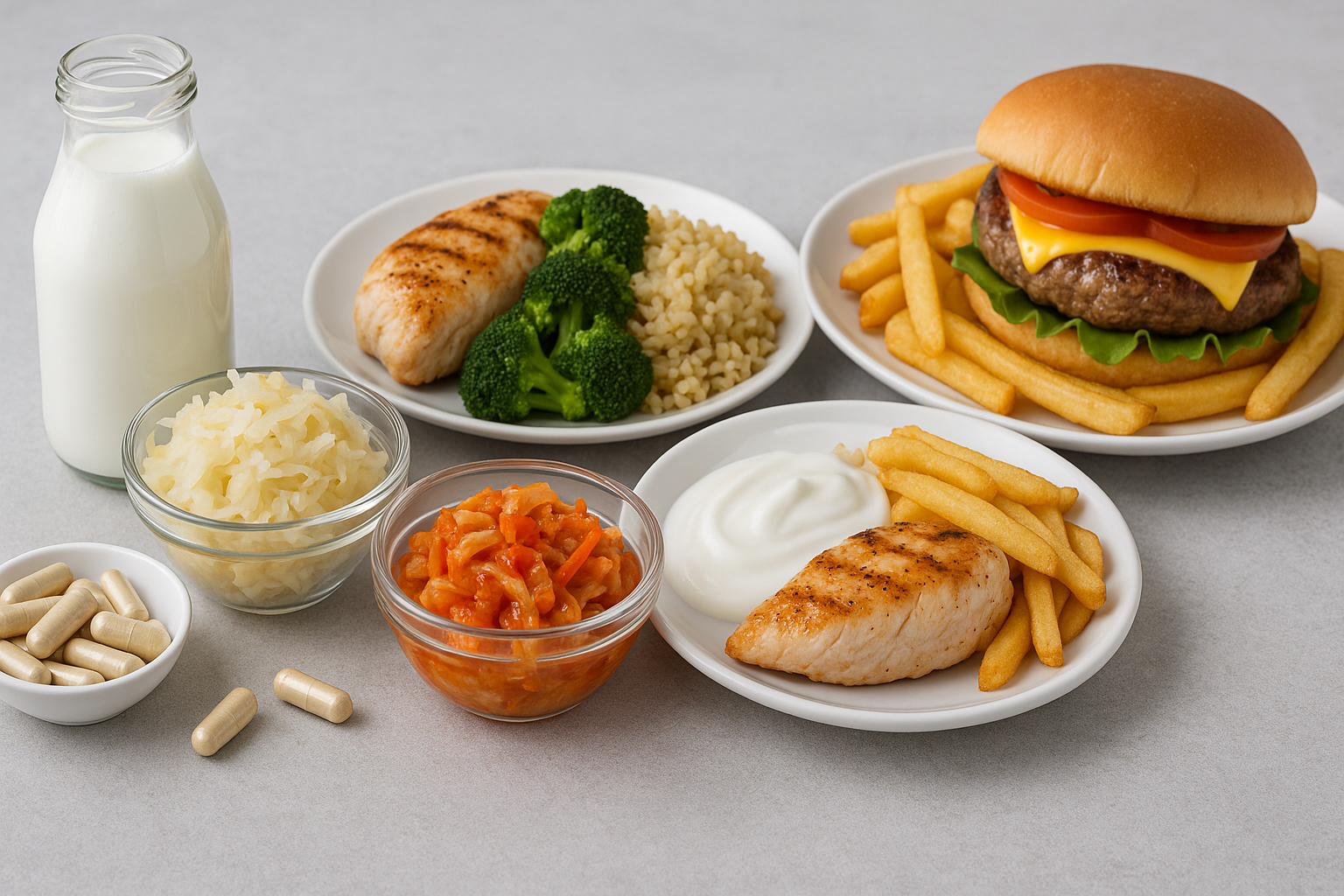

Leveraging Digestive Enzymes and Probiotics in a Bulking Meal Plan
Digestive health is often overlooked during bulking phases, yet it is foundational to nutrient absorption and meal tolerance. As your food intake increases, so does the demand on your digestive system. Bloating, sluggishness, or irregular bowel movements are signs that your gastrointestinal tract may need support.
Digestive enzymes, which help break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, can be particularly beneficial when eating larger meals. Supplementing with protease, amylase, and lipase may reduce discomfort and enhance nutrient absorption. Probiotic-rich foods like kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and yogurt support gut microbiota balance, improving immunity and inflammation control.
Including fermented foods in your bulking meals or taking a daily probiotic supplement can ensure your digestion remains efficient. This not only enhances physical comfort but also improves the availability of nutrients to your muscles, supporting better recovery and strength gains over time.
Using High-Calorie Liquid Meals to Meet Caloric Needs
Many people struggle to meet their bulking calorie goals through whole foods alone, particularly those with smaller appetites or fast metabolisms. Liquid meals and shakes offer a practical solution, as they are easier to digest and can be consumed quickly, even between meals.
The best bulking meals in liquid form include smoothies made with whole milk or plant-based alternatives, oats, bananas, nut butters, protein powder, and healthy oils like MCT or flaxseed. These shakes can easily exceed 800–1,000 calories per serving while providing balanced macros. Their portability also makes them ideal for busy professionals and students who may not have time to prepare a full meal.
Incorporating one or two calorie-dense liquid meals into your bulking diet program can be a game-changer, especially on training days when appetite suppression from workouts can reduce overall intake. Keep ingredients simple, whole, and aligned with your macro goals to avoid consuming empty calories.
Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms in Bulking Diets
Emerging research in chrononutrition reveals that when you eat may be nearly as important as what you eat. Synchronizing your bulking foods with your circadian rhythms—your body’s internal clock—can enhance metabolic efficiency, hormone regulation, and muscle protein synthesis.
Consuming a large portion of your daily calories earlier in the day can improve insulin sensitivity and energy levels. A front-loaded eating pattern with balanced breakfasts and lunches supports a more anabolic hormonal environment. This means eating protein-rich bulking meals within 60–90 minutes of waking up and again after training can maximize muscle-building potential.
Late-night eating isn’t inherently bad for bulking, especially if the foods are nutrient-dense and portion-controlled. However, be mindful of sleep quality and digestive comfort. Casein-rich bedtime snacks, such as Greek yogurt or cottage cheese, are excellent choices because they support overnight muscle repair without spiking blood sugar or causing restlessness.
The Role of Micronutrients and Fiber in Bulking Meals
While the focus during bulking often revolves around hitting calorie and protein goals, neglecting micronutrients can lead to deficiencies that impair performance, recovery, and overall well-being. Vitamins and minerals such as magnesium, zinc, B vitamins, and vitamin D are essential for hormone regulation, energy production, and muscle function.
Great bulking meals incorporate a variety of colorful vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to ensure a broad intake of essential nutrients. Leafy greens, berries, avocados, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes are nutrient-dense, calorie-efficient foods that also contribute to a healthy gut microbiome and immune system.
Fiber, too, plays a crucial role. Soluble fiber helps regulate blood sugar and cholesterol, while insoluble fiber supports digestion and gut health. Aim for at least 25–35 grams of fiber per day by incorporating foods such as oats, lentils, broccoli, apples, and flaxseeds into your bulking meal plan. Healthy digestion ensures your body absorbs the nutrients you’re working hard to consume and optimizes your training recovery.
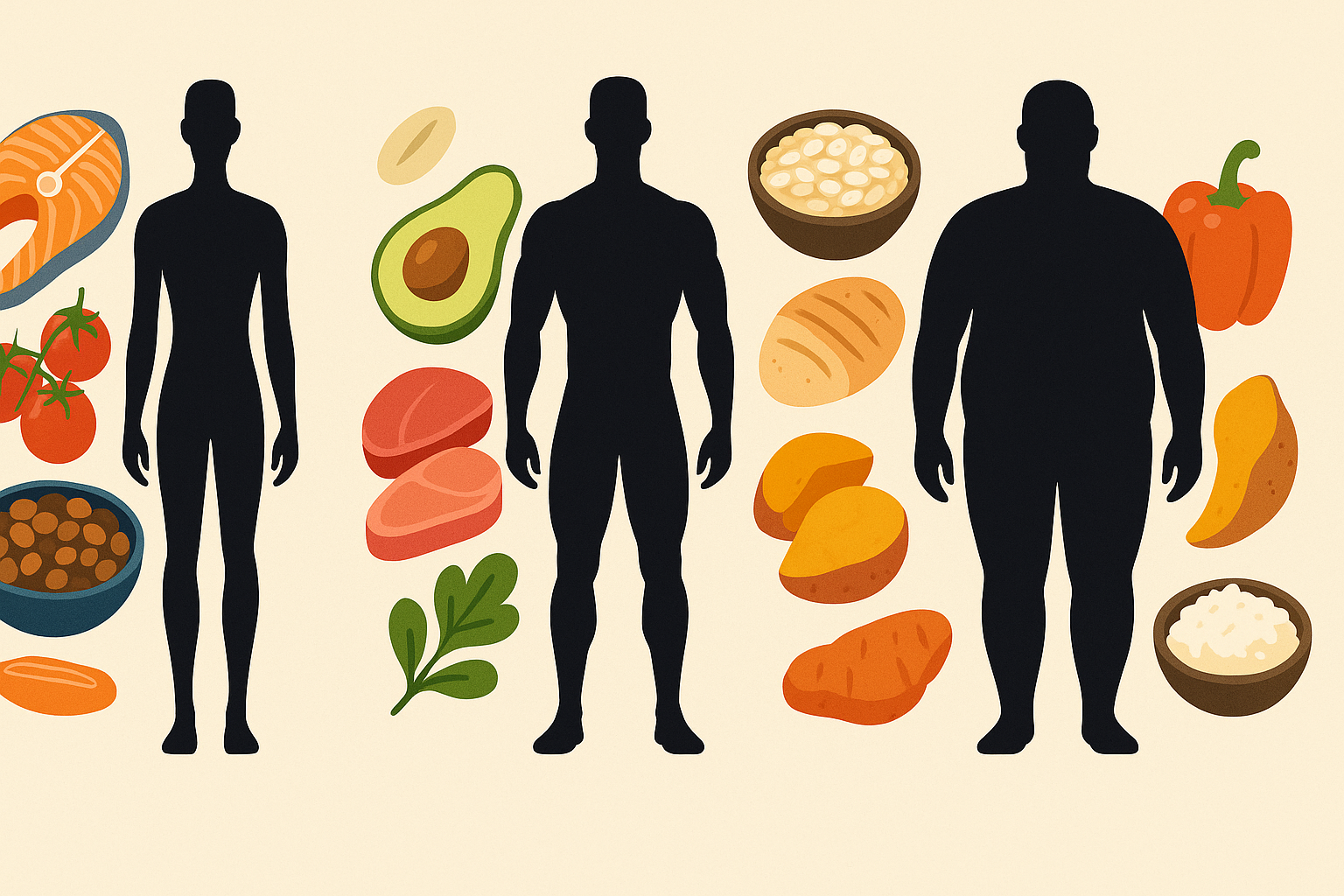

Bulking for Different Body Types and Metabolisms
Not all bodies respond to bulking diets in the same way. Ectomorphs, or naturally lean individuals with high metabolisms, may require more aggressive calorie increases and frequent meals to gain weight. Their bulking meals need to be calorie-dense, incorporating high-fat ingredients like oils, cheeses, and fatty fish, alongside starchy carbohydrates and proteins.
Endomorphs, who store fat more easily, should still maintain a caloric surplus but emphasize clean foods with high satiety, such as legumes, lean proteins, and fiber-rich vegetables. Their focus should be on moderate carbs and consistent weight training to ensure the surplus is directed toward muscle.
Mesomorphs, often considered the most athletic body type, may respond well to traditional bulking strategies. However, they too must monitor progress and make adjustments based on how their body changes. Understanding your body’s response to different foods, portion sizes, and training volumes is crucial in developing a sustainable and effective bulking strategy.
Bedtime Meals That Extend the Anabolic Window
Muscle growth doesn’t stop when you sleep, and eating the right foods before bed can extend your anabolic window. Casein-rich foods such as cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and casein protein shakes digest slowly, releasing amino acids steadily throughout the night. These good meals for bulking are essential for preventing overnight muscle breakdown.
A bedtime smoothie with casein protein, almond butter, banana, and flaxseed provides a slow-digesting, nutrient-rich option. Alternatively, a small bowl of oatmeal with cottage cheese and a sprinkle of cinnamon makes for a cozy and effective nighttime snack. Eggs or scrambled tofu with vegetables can also serve as a solid late meal for those with higher calorie demands.
Including a final feeding window in your bulking diet plan ensures that your muscles are constantly supplied with the building blocks they need, even during rest. It also helps maintain a positive nitrogen balance, which is crucial for muscle preservation and growth.
Putting It All Together: Your Complete Bulking Diet Program
The best bulking meals are more than just calorie-dense; they are nutrient-dense, satisfying, and strategically timed. A complete bulking diet program considers your individual calorie needs, macronutrient distribution, and daily schedule. Eating five to six meals a day, spaced three to four hours apart, helps keep energy levels high and muscle-building signals activated.
Meal prepping is key to staying on track. Cook proteins and carbohydrates in bulk, portion meals in containers, and have snacks readily available. Rotate meals to prevent palate fatigue and include a wide range of foods to ensure vitamin and mineral diversity. Supplements like whey protein, creatine, and omega-3s can support your bulking efforts but should never replace whole foods.
As you commit to a bulking meal plan, keep a food log or use an app to track progress and make necessary adjustments. Over time, your body will respond with increased strength, muscle size, and improved training performance. Always listen to your body’s hunger cues, recovery status, and digestion patterns to fine-tune your approach.
Frequently Asked Questions: Expert Insights on Building Muscle with a Bulking Diet
1. How can I optimize digestion when consuming large-volume bulking meals?
Digestive efficiency often becomes a challenge during a bulking phase, especially when meal volumes increase significantly to meet caloric targets. To minimize bloating and discomfort, it’s important to space your meals strategically and avoid overloading your digestive system in a single sitting. You can enhance digestion by including fermented foods like kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, which naturally provide probiotics to support gut health. Taking the time to chew thoroughly and eating more slowly can also help prevent gastrointestinal distress, allowing your body to better absorb nutrients from your bulking foods. Additionally, consider incorporating ginger, fennel, and peppermint into your meals to naturally stimulate digestive enzymes and reduce bloating.
2. What role does hydration play in supporting a successful bulking diet plan?
Hydration is often an underestimated factor in muscle growth, but it’s critical in maximizing the benefits of any bulking diet program. Water supports muscle function by facilitating nutrient delivery and waste removal, and dehydration can impair protein synthesis and recovery. During a bulking phase, where protein intake and thermogenesis are elevated, your kidneys require even more water to process excess nitrogen. Moreover, consuming high-fiber bulking foods increases your hydration needs to prevent constipation and maintain regular digestion. A good rule of thumb is to drink at least half your body weight in ounces of water daily, with increased intake on training days or when consuming particularly salty or dense bulking meals.
3. How do I maintain a clean bulking approach without gaining excessive fat?
Clean bulking involves creating a moderate caloric surplus using nutrient-dense, whole foods while minimizing processed, high-sugar options. The key to success lies in balancing your energy surplus—usually 250 to 500 extra calories per day—so that you support muscle growth without encouraging fat storage. Choosing the best bulking meals composed of lean proteins, complex carbs, and healthy fats helps keep blood sugar stable and promotes lean mass accrual. Monitoring body composition using skinfold calipers or DEXA scans can help track whether your weight gain is primarily muscle. You should also adjust your bulking meal plan every two to three weeks based on visual feedback, energy levels, and performance in the gym.
4. How do training variables impact my choice of bulking meals?
Your training style heavily influences your nutritional needs and, by extension, your bulking meals. For high-volume hypertrophy training, you’ll need more carbohydrates to fuel sessions and aid recovery, meaning meals should emphasize starchy vegetables, whole grains, and fruits. In contrast, strength-based or powerlifting routines may demand slightly higher fat intake for hormonal support, while still maintaining adequate carbohydrates. The timing of bulking meals should match your training frequency; for two-a-day sessions, consuming both pre- and post-workout bulking foods becomes essential. Recovery days should still include high-quality protein and moderate carbs to sustain anabolic signaling even when you’re not lifting.
5. What are some overlooked micronutrients that support effective bulking?
While most people focus on macronutrients in their bulking diet, key micronutrients can greatly impact progress. Zinc, for example, is crucial for testosterone production and immune function, both of which influence recovery and muscle building. Magnesium supports muscle contraction and quality sleep, which is when most muscle growth occurs. B-complex vitamins enhance energy metabolism, helping your body convert bulking foods into usable energy for workouts. Finally, potassium and sodium are vital for fluid balance and muscle hydration, especially when training intensely. Prioritizing whole foods like leafy greens, sweet potatoes, avocados, and seafood ensures that your bulking diet program supports both macro and micronutrient needs.
6. How can I adapt bulking meals for plant-based or vegetarian diets?
Plant-based athletes can absolutely succeed with a bulking meal plan by being strategic with their food pairings and caloric density. Legumes, lentils, tempeh, tofu, seitan, and soy milk are excellent protein-rich bulking foods that also provide fiber and micronutrients. Combining foods like rice and beans or hummus with whole grain pita can create complete protein profiles. Healthy fats like nuts, seeds, and avocado not only provide satiety but also add necessary calories without excessive volume. Nutritional yeast, fortified cereals, and algae-based omega-3 supplements can fill in nutrient gaps often associated with vegan bulking diets. A well-constructed vegetarian or vegan bulking diet plan can be just as effective as an omnivorous one when properly balanced.
7. Do good meals for bulking differ based on training goals like hypertrophy vs. powerlifting?
Absolutely—your ideal bulking meals will vary based on your specific training goals. For hypertrophy-focused athletes, meals rich in carbohydrates and moderate in fat are essential to fuel volume-heavy sessions and promote glycogen storage. These meals might include grilled chicken, brown rice, and avocado or a smoothie with oats, whey protein, and banana. For powerlifters focusing on maximal strength, slightly higher fat content can support testosterone production, and timing meals around heavy lifts can aid neurological recovery. In both cases, the inclusion of sufficient protein remains non-negotiable, but meal composition and timing should align with your periodization and training frequency. The best foods for bulking are always customized to support your workload, whether it’s eight reps or a one-rep max.
8. What makes the best bulking meals suitable for long-term adherence?
Consistency is the cornerstone of a successful bulking diet plan, and that requires meals that are not only nutritionally dense but also enjoyable, convenient, and satisfying. The best bulking meals strike a balance between flavor and function—think of chili made with lean beef, beans, and olive oil, or a chicken stir-fry with brown rice and peanut sauce. Variety is also key to long-term adherence, so rotating proteins (e.g., turkey, salmon, eggs), carbohydrates (e.g., quinoa, oats, sweet potatoes), and spices keeps meals exciting. Convenience plays a role as well—meal prepping in batches and using slow cookers or air fryers helps reduce cooking fatigue. Ultimately, great bulking meals support physical performance while fitting into your personal tastes and lifestyle habits.
9. How does metabolic adaptation affect my bulking progress over time?
Metabolic adaptation is the body’s natural response to sustained changes in energy intake. As you gain lean mass, your resting metabolic rate increases, which means your caloric needs rise even during rest. However, if progress stalls despite eating what worked before, it may be due to increased non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT) or digestive efficiency. In such cases, reassessing your bulking meal plan and gradually increasing intake may be necessary. Keep an eye on recovery, mood, and strength levels, and don’t be afraid to recalibrate your bulking diet to meet your evolving metabolism. This dynamic process underscores why even the best foods for bulking require periodic reevaluation.
10. How do social and psychological factors influence adherence to a bulking diet program?
Sticking to a bulking diet program involves more than just meal prep—it requires mental discipline and emotional resilience, especially when physical changes challenge your self-image. Some individuals may struggle with seeing their abs fade or dealing with unsolicited comments about weight gain. It’s crucial to reframe bulking as a deliberate, science-based phase that supports long-term transformation. Social events can be navigated by choosing high-protein menu options or bringing your own good meals for bulking that align with your goals. Support from like-minded individuals—whether through a coach, training partner, or online community—can provide the encouragement needed to maintain motivation and purpose.
Conclusion: Fueling Muscle Growth with the Best Bulking Meals
Muscle growth doesn’t happen by chance. It requires deliberate, consistent action—especially when it comes to nutrition. Integrating the best bulking meals into your daily routine provides your body with the tools it needs to grow stronger, faster, and more resilient. From breakfast to bedtime, every meal plays a critical role in optimizing your bulking diet.
Choosing great bulking meals filled with high-quality proteins, smart carbohydrates, and healthy fats ensures that you’re not just eating more but eating better. Whether you’re prepping for a competition or simply pursuing a more muscular physique, the quality of your bulking meals can define the outcome.
By implementing the bulking strategies, foods, and meal plans outlined here, you’ll be well-equipped to maximize gains and fuel long-term success. Trust the process, stay consistent, and let every forkful of food bring you one step closer to your goals.