Unlocking Peak Potential: Introduction to Strength for the Physically Fit
Among guys with fit bodies, the pursuit of greater strength and performance becomes more than just a goal—it transforms into a mindset, a continuous journey of physical refinement and personal mastery. These individuals already boast well-conditioned physiques, sculpted through years of dedication to proper nutrition, effective training regimens, and consistent discipline. Yet, for those who have reached this advanced stage of fitness, the challenge lies not in building a foundation, but in maximizing potential. Strength training is not simply about lifting heavier weights; it’s about strategically applying science-backed techniques that enhance muscular efficiency, neuromuscular control, and metabolic performance. For fit body men, the nuances of programming, recovery, and intensity become critical factors that separate a strong body from a truly powerful one.
Understanding the specific training needs of a body fit man requires a shift from general fitness principles to more advanced performance strategies. At this level, the body adapts more slowly to stimulus, making intelligent progression and strategic variability vital to continued success. Moreover, the demands of a fit male body include a balanced focus on hypertrophy, functional strength, cardiovascular health, and mobility—all of which must work synergistically to support long-term fitness gains. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore cutting-edge methodologies designed to elevate muscular capacity and optimize performance, tailored specifically for those who already exhibit the hallmarks of a male gym body.
You may also like: The Ultimate 30-Day Workout Plan for Men Working Out in the Gym: Proven Full Body Strength Exercises to Maximize Results
Why Strength Training Matters for Fit Male Bodies
Even for individuals who appear to have reached their peak physical form, strength training remains essential. A well-developed body may suggest strength, but without targeted resistance work, even the most aesthetically pleasing physique can lack the raw power, endurance, and resilience needed for real-world performance. Muscle hypertrophy, for instance, doesn’t always equate to muscle strength; large muscles may still underperform if neuromuscular coordination and tendon strength are neglected. Thus, for those possessing a normal fit body male physique, the journey to enhanced performance requires a scientific understanding of load management, movement patterns, and training specificity.
Strength training for these individuals supports more than just muscular growth. It reinforces joint integrity, enhances metabolic health, and contributes significantly to hormone optimization. Testosterone and growth hormone levels, critical for sustaining lean mass and vitality, are stimulated by high-intensity resistance exercises such as compound lifts, isometrics, and eccentric overload. These benefits, however, can only be fully realized when the training program is customized to an already developed physique.
Moreover, for fit body men striving to maintain or even elevate their physical edge, strength training can introduce the variability and intensity necessary to break through adaptation plateaus. With carefully programmed progressive overload, varied repetition schemes, and advanced periodization models, muscle systems are continually challenged to evolve. This keeps the male gym body not only visually impressive but functionally exceptional across a spectrum of performance markers.

Key Strength Principles for Guys with Fit Bodies
For guys with fit bodies, the underlying principles of strength training must go beyond the basics of sets and reps. The focus shifts toward efficiency, intensity, and specificity. One of the most critical principles is mechanical tension, which involves lifting heavy loads through a full range of motion to stimulate muscle fibers deeply. At this level, ensuring mechanical tension while preserving joint health requires mastery of technique and periodization.
Another essential concept is muscle fatigue management. Highly trained individuals are more capable of pushing their central nervous system to its limits, increasing the risk of overtraining. A strategic approach to fatigue—using deload weeks, autoregulated volume, and variable intensity techniques like wave loading or cluster sets—is crucial for long-term progression. For the normal fit body male, knowing when to scale back is just as important as knowing when to push harder.
Progressive overload also requires a more nuanced approach. Instead of simply adding weight to the bar, experienced lifters benefit from manipulating tempo, time under tension, and exercise complexity. This could mean transitioning from traditional barbell squats to Bulgarian split squats, or from regular pull-ups to weighted variations. Each of these methods provides new challenges that stimulate strength gains while preserving muscular balance and joint stability.

Periodization Strategies to Maximize Muscle and Power
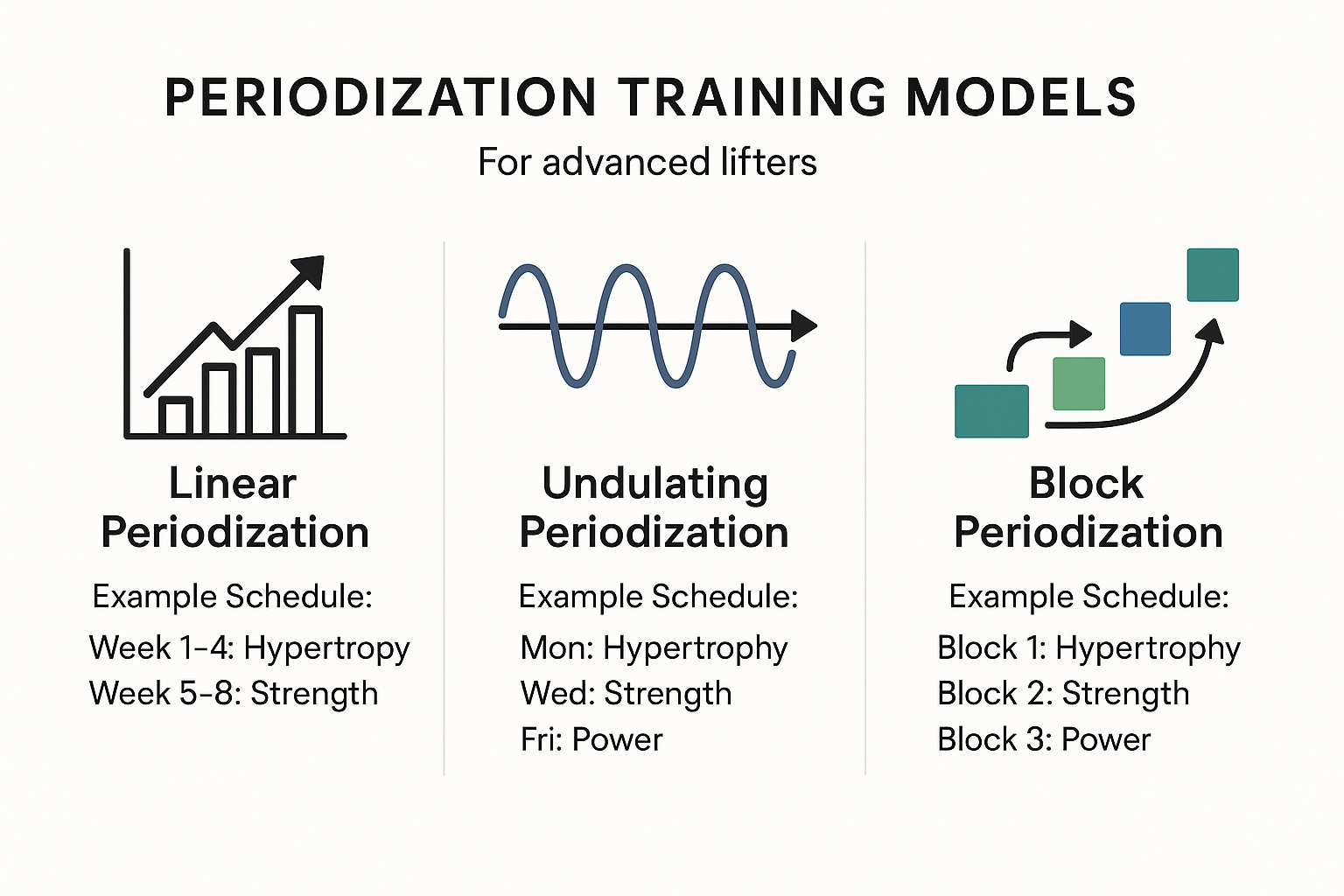
When dealing with a body fit man who is already accustomed to regular training, one of the most valuable tools is periodization—the structured manipulation of training variables over time to prevent plateaus and overtraining. Periodization helps to align physical goals with physiological needs, ensuring continual progress and minimizing injury risk.
Linear periodization, while effective for beginners, may lack the complexity needed by advanced lifters. Undulating periodization—where volume and intensity vary throughout the week—offers better adaptation for experienced trainees. For example, a fit male body might respond better to a heavy squat day followed by a dynamic effort day, and then a hypertrophy-based session, all within the same week.
Block periodization divides training into distinct phases: accumulation (volume-focused), intensification (strength-focused), and realization (peak performance). This approach works particularly well for guys with fit bodies because it allows for targeted adaptations based on their goals, whether it’s increasing their one-rep max or developing explosive athleticism.
Auto-regulated periodization introduces flexibility by using subjective feedback, such as Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) or bar velocity tracking. This method ensures that training remains effective even when external factors like sleep, stress, or diet vary. For those already exhibiting a male gym body, this adaptability is vital to optimize each training session without overreaching.
Nutrition Strategies to Support Strength and Definition
A powerful physique isn’t built in the gym alone; it is sculpted and fueled through strategic nutrition. For fit body men, whose metabolic efficiency and caloric needs differ from those starting their fitness journey, tailoring macronutrient intake is essential. Protein remains the cornerstone of muscle repair and hypertrophy, with research suggesting 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day for optimal results. However, protein timing and distribution matter just as much, ensuring amino acid availability throughout the day and post-training.
Carbohydrates are crucial not only for energy but also for recovery and performance. For the body fit man, carbs help replenish glycogen stores, regulate hormone production, and fuel high-intensity training. Complex sources like oats, quinoa, sweet potatoes, and fruits offer sustained energy, while quick-digesting carbs around workouts enhance immediate fuel availability and recovery.
Fats play an essential role in hormonal health, particularly testosterone synthesis. Incorporating healthy fats from avocado, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish supports endocrine function and reduces systemic inflammation. Micronutrients like magnesium, zinc, and vitamin D are also critical for muscle function, recovery, and performance.
Meal timing and nutrient partitioning are advanced strategies for fit body men. Consuming a balanced meal 60 to 90 minutes before training ensures adequate energy availability, while a post-workout meal rich in protein and carbs initiates the recovery process. Additionally, techniques like carb cycling or intermittent fasting may offer further body composition refinement without compromising strength.
Advanced Recovery Techniques for Fit Male Bodies
Recovery becomes increasingly important as training intensity and volume rise. For the fit male body, simple rest days may not suffice. Advanced recovery methods help manage inflammation, restore neural drive, and prepare the muscles and connective tissues for subsequent sessions. Among these, active recovery through low-intensity cardio, mobility work, or swimming promotes blood flow and reduces delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS).
Cold water immersion and contrast therapy (alternating hot and cold baths) are used by many elite athletes to improve circulation and decrease muscle stiffness. While scientific consensus on their efficacy is mixed, many experienced lifters report subjective improvements in recovery quality. Foam rolling and myofascial release, particularly when paired with dynamic stretching, enhance range of motion and reduce muscle tightness.
Sleep remains the most powerful and accessible recovery tool. For guys with fit bodies, maintaining 7 to 9 hours of high-quality sleep is essential for optimizing hormone release, neurological recovery, and muscle repair. Blue light management, consistent sleep schedules, and pre-bed rituals all support improved sleep hygiene.
Finally, understanding biofeedback cues—such as heart rate variability (HRV), resting heart rate, mood, and perceived exertion—can guide training adjustments. When fatigue accumulates, incorporating light days, adjusting volume, or focusing on recovery modalities can prevent overreaching and support long-term gains.
Essential Strength Exercises for Guys with Fit Bodies
Certain compound exercises remain foundational for developing maximum strength. Squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and overhead presses are timeless for a reason—they engage multiple muscle groups and stimulate systemic hormonal responses. However, for guys with fit bodies, refining these movements through tempo changes, variable grips, and equipment (such as resistance bands or chains) can provide continued progression and reduced injury risk.
Front squats, Romanian deadlifts, deficit deadlifts, and incline presses offer variation without sacrificing stimulus. These exercises challenge the body in novel ways, increasing coordination and core engagement. Single-leg exercises such as Bulgarian split squats and pistol squats improve balance, reduce muscular asymmetry, and enhance athleticism.
Olympic lifts like the clean and jerk or snatch introduce power development and coordination. While they require technical proficiency, even variations like hang cleans or push presses can be incredibly effective for trained lifters. For a male gym body, incorporating explosive movements develops Type II muscle fibers and accelerates strength development.
Accessory exercises should not be overlooked. Pull-ups, dips, hip thrusts, and face pulls help strengthen supporting muscles and prevent imbalances. Rotator cuff strengthening, scapular control, and posterior chain reinforcement are all vital to maintaining joint health and muscular harmony in a well-trained body.

Programming Split Options for Optimal Results
Designing an effective training split is key to long-term success. For a normal fit body male, options such as upper/lower splits, push-pull-legs, or full-body training can be tailored based on goals, schedule, and recovery capacity. Each has its advantages, and the best approach often rotates over time.
Upper/lower splits allow for higher frequency and recovery, ideal for increasing both strength and hypertrophy. Push-pull-legs splits create a natural division between movement patterns, enabling focused sessions and increased training volume per muscle group. Full-body training, performed three to four times weekly, works well for maintaining strength while integrating other physical goals like conditioning or mobility.
Weekly periodization should reflect both progression and deloading. For example, three weeks of progressive overload followed by a reduced-intensity week allows the body to adapt without stagnation. Varying rep schemes—from strength-based (3 to 5 reps) to hypertrophy (8 to 12 reps)—within each cycle ensures complete muscular development.
Ultimately, the ideal program is dynamic, not static. Tracking progress, listening to the body, and adjusting based on recovery metrics and performance data will yield the best results. Flexibility and structure must coexist to support the physical and psychological demands placed on fit body men.
Hormonal and Metabolic Optimization for Fit Athletes
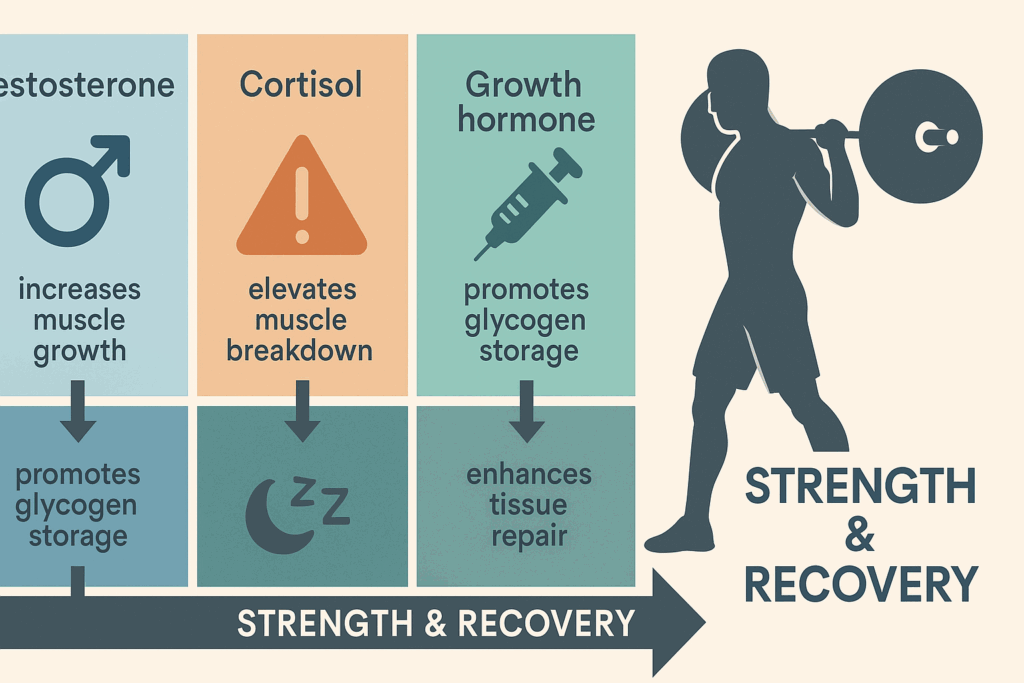
Advanced strength training demands hormonal and metabolic balance. Testosterone, growth hormone, cortisol, and insulin all influence strength, recovery, and body composition. Guys with fit bodies often hover near peak performance levels, but without proper management, stress, overtraining, and dietary imbalances can disrupt these hormones.
Weight training, particularly with compound lifts at high intensity, naturally boosts testosterone and growth hormone. However, excessive volume or lack of recovery elevates cortisol, which can counteract muscle growth and promote fat retention. Balancing stressors through sleep, recovery, and mindfulness practices is therefore non-negotiable.
Nutritional timing also supports hormonal regulation. Protein and healthy fats at breakfast help reduce cortisol spikes, while post-workout carbs blunt cortisol and elevate insulin, aiding in muscle protein synthesis. Zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3s are especially helpful in maintaining hormonal equilibrium.
Metabolic health is equally critical. Insulin sensitivity allows for efficient nutrient partitioning, directing calories toward muscle rather than fat. Strategies like fasted cardio, intermittent fasting, or low-glycemic carbohydrate selection may enhance metabolic flexibility. Maintaining a lean physique with good energy levels depends on this delicate hormonal and metabolic balance.
Functional Conditioning for Physically Fit Guys
Strength without endurance, agility, or mobility limits real-world performance. For guys with fit bodies, integrating functional conditioning ensures the body is not only strong but adaptable. Functional training includes movements that mimic daily or sport-specific activities, combining strength with balance, coordination, and agility.
Kettlebell swings, sled pushes, battle ropes, and loaded carries train power endurance and grip strength. These movements bridge the gap between traditional lifting and athletic performance. Plyometrics such as box jumps or medicine ball throws increase explosive output and tendon resilience.
Mobility work keeps joints healthy and muscles elastic. Dynamic stretching, yoga, or mobility flows before and after training reduce injury risk and improve range of motion. Incorporating regular assessments (e.g., Functional Movement Screen) helps identify restrictions and tailor mobility efforts accordingly.
By layering functional conditioning into a traditional strength plan, guys with fit bodies maintain versatility and durability—qualities essential for long-term performance across any physical discipline.

Frequently Asked Questions for The Ultimate Strength Guide for Guys with Fit Bodies to Build Muscle and Boost Performance
1. What are the most overlooked recovery strategies for fit male bodies?
While many athletes prioritize sleep and nutrition, some of the most overlooked recovery techniques for a fit male body include structured breathing exercises, vagus nerve stimulation, and active neural reset therapy. Controlled diaphragmatic breathing, practiced daily, can reduce cortisol levels and improve parasympathetic activation, promoting deeper recovery. Vagus nerve stimulation through cold exposure or humming exercises enhances systemic relaxation and resilience. Neural reset therapy, which targets motor patterns and muscle inhibition, is particularly effective for body fit men facing chronic stiffness or movement asymmetries. These strategies, though lesser-known, offer measurable improvements in readiness, flexibility, and long-term muscular resilience.
2. How can guys with fit bodies stay motivated after reaching a strength plateau?
For guys with fit bodies, hitting a plateau can feel demotivating, especially when physical changes become less visible over time. To sustain engagement, shifting focus from aesthetic goals to performance benchmarks—such as increasing vertical jump height or improving 3-rep max lifts—can reignite purpose. Competitive outlets like local lifting meets, CrossFit challenges, or recreational sports help reframe training as a skill-based pursuit. Implementing a deload and mental reset period every few months prevents burnout and restores passion. Finally, collaborating with other fit body men in group training environments builds camaraderie and reinvigorates progress through friendly competition and shared goals.
3. Should fit body men modify their lifting form as they age?
Yes, adapting lifting technique with age is essential, even for individuals maintaining a male gym body into their 40s and beyond. Joint wear, connective tissue elasticity, and recovery speed all shift with time, requiring safer biomechanical patterns. For instance, using a trap bar instead of a straight bar for deadlifts reduces spinal shear force without compromising gains. Similarly, switching from behind-the-neck presses to neutral-grip dumbbell presses lowers shoulder strain while preserving upper-body development. Periodic movement assessments can highlight areas where mobility or motor control has diminished. The goal for the normal fit body male over time is to extend training longevity while minimizing injury risk without sacrificing intensity.
4. How can a body fit man prevent overuse injuries during intense programming?
Overuse injuries often plague dedicated lifters because their consistency outpaces their joint’s tolerance to repetitive stress. To avoid this, body fit men should incorporate weekly movement variability, such as swapping bilateral squats with split squats or barbell rows with ring rows. Integrating weekly soft tissue work through massage or instrument-assisted release counters fascial restrictions that lead to compensation patterns. Deliberately cycling off certain lifts for several weeks per quarter—a technique known as exercise rotation—helps mitigate tissue overload. Monitoring biofeedback markers like sleep quality, mood, and grip strength can also serve as early warnings. Implementing these safeguards preserves the integrity of a fit male body across training cycles.
5. What psychological factors influence training consistency in fit body men?
Psychological resilience plays a significant role in the training consistency of fit body men. Discipline becomes habit when paired with identity reinforcement, meaning individuals who perceive themselves as high performers are more likely to adhere to routines. Visualization techniques, when practiced regularly, prime the brain for confident performance under heavy loads. Intrinsic motivation is strengthened when training goals align with personal values—such as being a strong role model for family or performing better in a chosen sport. Additionally, journaling about training outcomes or emotional responses helps normalize setbacks and prevent discouragement. Developing emotional intelligence in fitness can be just as vital as physical strength.
6. How does travel impact muscle retention in guys with fit bodies?
Frequent travel can disrupt both training consistency and muscle retention, especially among guys with fit bodies who rely on structured routines. However, strategic planning helps mitigate these effects. Resistance bands and suspension trainers allow for effective hotel room workouts that maintain neuromuscular stimulation. Prioritizing compound bodyweight movements like pistol squats, single-arm pushups, and wall walks helps preserve strength without requiring a gym. Nutritionally, carrying portable protein options and hydrating aggressively combat catabolism and jet lag. Adjusting sleep patterns to the local time zone within 24 hours of arrival supports hormonal regulation, which is critical to sustaining muscle mass. Overall, a mobile training mindset ensures a consistent fitness standard regardless of geography.
7. What are some lesser-known supplements that benefit the normal fit body male?
Beyond protein, creatine, and caffeine, several lesser-known supplements can benefit the normal fit body male. Betaine anhydrous supports muscular endurance and may improve power output in resistance-trained individuals. Ashwagandha, an adaptogen, has been shown to reduce cortisol while subtly enhancing strength and testosterone. L-citrulline can improve nitric oxide production, leading to better blood flow and muscular endurance during high-rep sessions. Curcumin, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, assists recovery and joint health. When used thoughtfully, these supplements add measurable value to a body fit man’s performance and recovery strategy, especially when dietary habits alone cannot fulfill specific physiological demands.
8. How can guys with fit bodies optimize their hormones naturally?
Optimizing hormones naturally is essential for maintaining strength, energy, and mental clarity in guys with fit bodies. Regular exposure to sunlight, particularly in the morning, helps regulate circadian rhythms and supports healthy testosterone production through vitamin D synthesis. Resistance training with a focus on compound movements performed at high intensity enhances growth hormone and testosterone release. Limiting exposure to endocrine disruptors, found in some plastics and grooming products, also helps preserve hormonal balance. Prioritizing deep sleep and avoiding blue light exposure in the evening has a profound impact on cortisol regulation. Collectively, these habits create an internal environment conducive to optimal performance and recovery.
9. What training adaptations help sustain a male gym body during periods of high stress?
During high-stress periods, maintaining a male gym body requires strategic training adaptations to preserve muscle while preventing burnout. Reducing training volume while maintaining intensity—for example, shifting to three full-body sessions per week—allows for sufficient stimulus without exacerbating fatigue. Incorporating more autoregulated training, where effort is based on daily energy levels, provides needed flexibility. Emphasizing eccentric tempos or isometric holds maintains muscle tension even with lighter loads. Adding brief recovery-focused sessions, like mobility flows or light circuits, ensures that the nervous system stays primed. Most importantly, aligning workouts with personal bandwidth helps maintain a balanced physique without compounding psychological stress.
10. Why long-term planning matters for guys with fit bodies focused on performance?
Long-term planning is critical for guys with fit bodies who seek not just short-term aesthetics but lasting performance. Without a strategic outlook, training becomes reactive, increasing the risk of stagnation or overuse injury. Structured annual programming—incorporating phases of hypertrophy, strength, power, and active recovery—provides a sustainable path to continual growth. It also allows for periodized nutritional strategies, such as strategic bulking or recomp cycles, aligned with training phases. Mentally, long-term goals cultivate patience and purpose, reducing the temptation to make impulsive changes based on social media trends. In this way, a well-developed fit male body becomes not just a seasonal achievement but a lifestyle expression of discipline and excellence.
Conclusion: Sustaining Strength and Performance in Fit Male Bodies
Strength is not a destination but a dynamic process that evolves with the individual. For guys with fit bodies, building muscle and boosting performance is a high-level pursuit requiring intelligence, discipline, and adaptability. From progressive training methods to nutrient timing and recovery optimization, every detail matters when pushing the boundaries of what a conditioned body can achieve.
Through a focused understanding of programming, hormonal balance, functional mobility, and intelligent recovery, the male gym body transforms from simply aesthetic to exceptionally capable. Embracing this journey involves continuous self-assessment, education, and a willingness to adjust tactics as the body changes and goals evolve.
Ultimately, sustaining strength and enhancing performance is a lifelong endeavor. The insights presented here offer a roadmap tailored for those who already possess a solid physical foundation and seek to ascend even further. When applied consistently, these strategies ensure that fit body men not only maintain their elite form but elevate their potential to its absolute peak.
Further Reading:
What Are the Three Male Body Types?