Understanding the connection between hydration and hormones offers an often-overlooked perspective on men’s and women’s health. In particular, many people are asking: does drinking water increase testosterone? As testosterone plays a crucial role in regulating muscle mass, bone density, libido, energy levels, and overall well-being, exploring any potential ways to support its levels naturally is essential. This article dives deep into the physiological, nutritional, and biochemical relationships between hydration status and testosterone regulation, while also unpacking what science says about the broader impact of water on hormonal health.
You may also like : How Long Does Testosterone Stay in Your System? Effects, Duration, and What to Expect
The Biological Basis of Testosterone Production
Testosterone, the primary androgen hormone, is synthesized in the Leydig cells of the testes in men and in smaller amounts in the ovaries and adrenal glands of women. Its regulation is controlled by the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, a feedback loop that includes the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonads. The secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary stimulates the Leydig cells to produce testosterone. This process is highly sensitive to a variety of physiological factors including stress, nutrient intake, sleep quality, and hydration.
Hydration plays a fundamental role in maintaining homeostasis, which includes optimal function of the endocrine system. A well-hydrated body ensures efficient transport of hormones, nutrients, and waste products. Conversely, even mild dehydration can lead to increased levels of cortisol, a stress hormone known to suppress testosterone production. By ensuring adequate fluid intake, the body may indirectly support testosterone synthesis by maintaining hormonal balance and reducing the inhibitory effects of cortisol.
Does Drinking Water Increase Testosterone? Exploring the Evidence
To address the core question—does drinking water increase testosterone?—we must examine the evidence through multiple lenses. While direct clinical trials isolating water intake as the sole variable influencing testosterone are limited, a wealth of indirect evidence supports the connection.
One study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that dehydration reduced performance and testosterone levels in athletes during training. The reduction in plasma volume from dehydration caused an increase in cortisol and a decrease in testosterone, supporting the theory that hydration status influences hormonal outcomes. Although this study focused on short-term athletic performance, it points to the broader implications of hydration for testosterone regulation.
Furthermore, animal studies have shown that dehydration can lead to disruptions in endocrine function, including alterations in testosterone levels. For example, research on rodents has revealed that chronic dehydration impairs testicular function and reduces serum testosterone. While extrapolation to humans requires caution, these results underscore the significance of maintaining hydration for hormonal stability.
Hydration and Cortisol: The Indirect Hormonal Interplay
One of the strongest links between hydration and testosterone lies in the balance between cortisol and testosterone. Cortisol and testosterone have an inverse relationship—when cortisol levels are elevated due to physical or psychological stress, testosterone levels tend to decline.
Hydration status significantly influences cortisol levels. Dehydration is a physiological stressor that stimulates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, increasing the secretion of cortisol. Elevated cortisol can interfere with the HPG axis, suppressing LH secretion and, consequently, testosterone production. Therefore, drinking adequate water can help modulate cortisol levels, indirectly supporting healthy testosterone levels.
This hormonal interplay has practical applications for athletes and active individuals. Maintaining hydration before, during, and after exercise can prevent spikes in cortisol that may otherwise impair muscle recovery, performance, and testosterone synthesis. For those using testosterone boosters or testosterone pills for men, hydration may optimize their efficacy by creating a favorable hormonal environment.
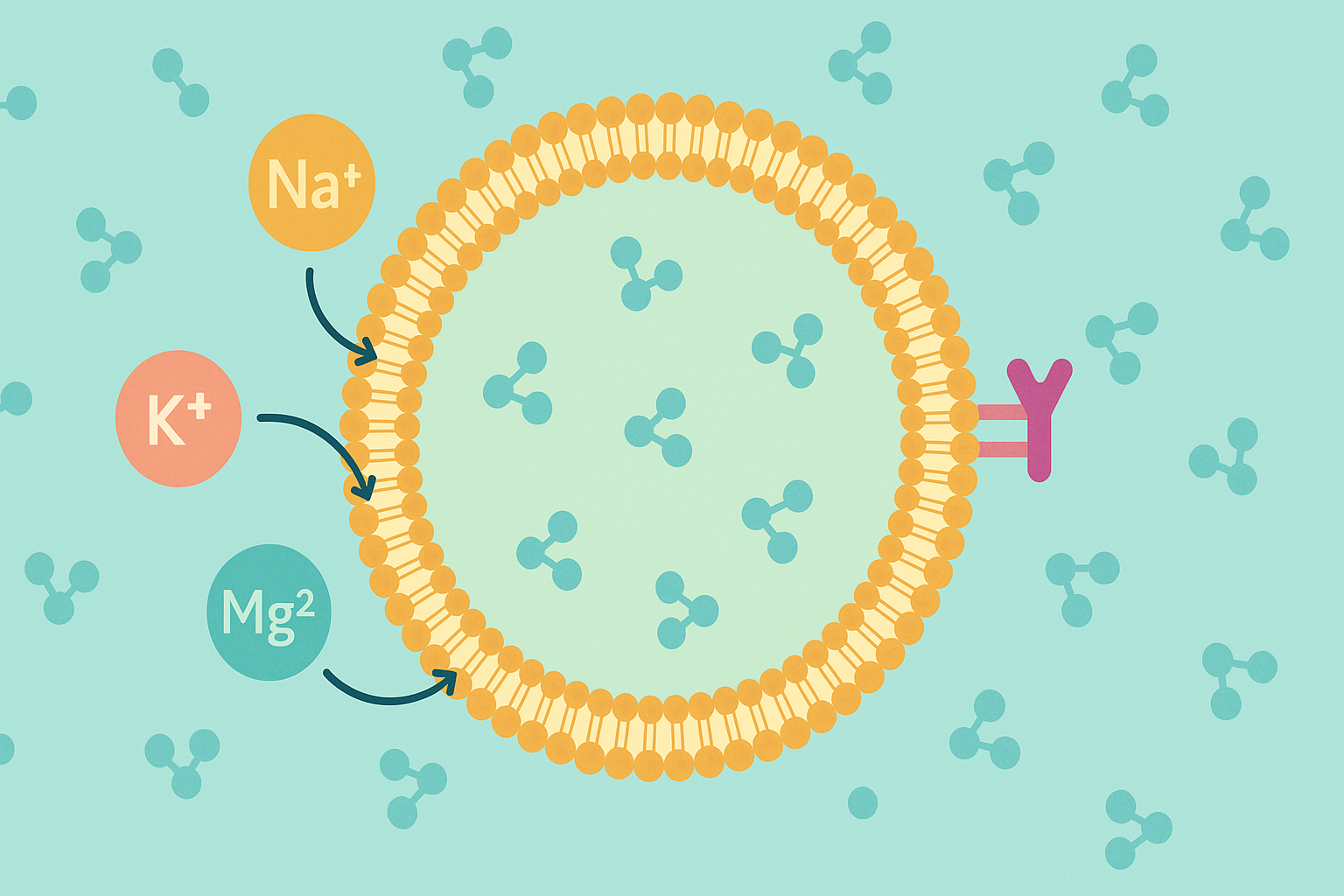
Electrolyte Balance and Hormonal Health
Hydration is not just about water intake; it also involves the balance of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These minerals are vital for cellular function, nerve transmission, and hormonal signaling. Imbalances can lead to suboptimal testosterone levels.
Magnesium, for example, is a co-factor in over 300 enzymatic reactions, many of which are related to testosterone production. Studies have shown that athletes with higher magnesium intake tend to have higher testosterone levels. Proper hydration supports electrolyte absorption and transport, ensuring that these minerals can perform their physiological functions effectively.
Furthermore, dehydration can alter the concentration of electrolytes in the blood, impairing the electrical gradients necessary for the function of the HPG axis. By staying hydrated, the body maintains a stable internal environment conducive to hormonal balance, reinforcing the importance of fluid intake alongside nutrient-rich diets for optimizing testosterone levels.
How Dehydration Impacts Energy, Libido, and Muscle Mass
Chronic dehydration can have far-reaching consequences that go beyond testosterone levels alone. Energy levels, libido, and muscle mass—three hallmarks of testosterone activity—are all negatively affected by inadequate fluid intake.
Energy metabolism relies on efficient cellular processes that require water for ATP production, nutrient transport, and thermoregulation. Dehydration slows these processes, leading to fatigue and decreased exercise performance. Low energy and poor exercise output can diminish the natural stimuli that promote testosterone production, such as strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Libido is another area intricately linked to both testosterone and hydration. Reduced blood volume due to dehydration can impair circulation, including to reproductive organs. Lower blood flow may contribute to erectile dysfunction or diminished sexual desire, conditions often associated with low testosterone.
Muscle mass also depends on both testosterone and hydration. Testosterone stimulates protein synthesis, while hydration ensures adequate delivery of amino acids and oxygen to muscle tissues. Dehydration reduces muscle pump, decreases strength, and can even increase the risk of injury. For individuals using testosterone supplements for men or the top testosterone booster, hydration remains a foundational factor in maximizing their effects.
Does Drinking Water Increase Testosterone in Women?
Although testosterone is often associated with men, women also produce this hormone in smaller amounts, and it plays a critical role in bone density, mood regulation, and libido. For women, the question of “does drinking water increase testosterone?” is equally relevant, especially in the context of natural hormonal health.
The same mechanisms that apply to men—hydration supporting hormone transport, reducing cortisol, and maintaining electrolyte balance—also apply to women. Furthermore, studies have suggested that dehydration may influence estrogen and progesterone levels, indirectly affecting testosterone through complex hormonal feedback loops.
For women looking to improve hormone balance naturally, focusing on hydration is a simple yet powerful strategy. This is particularly relevant for those interested in how to increase testosterone in females naturally. Combined with resistance training and adequate intake of zinc and vitamin D, hydration can support a healthy endocrine profile.
Hydration and Nutrition: A Synergistic Approach to Testosterone
Nutrition and hydration are inseparable when it comes to hormonal health. Foods that boost testosterone often contain high amounts of zinc, magnesium, healthy fats, and antioxidants. These include red meat, eggs, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens. However, without proper hydration, the absorption and metabolism of these nutrients may be impaired.
Water aids in digestion, nutrient transport, and enzymatic reactions that support hormone production. For example, does red meat boost testosterone? Yes, in part because of its zinc content, but only when digested and metabolized efficiently. Similarly, does protein boost testosterone? Absolutely, but its benefits are fully realized only when the body is adequately hydrated to utilize amino acids effectively.
Thus, hydration enhances the effectiveness of testosterone-supportive foods and supplements. Whether someone is exploring how to naturally increase testosterone or using a testosterone booster for man, integrating water with a nutrient-dense diet yields the best results.
Testosterone Supplements, Boosters, and the Role of Water
The market for testosterone boosters is vast, with numerous products claiming to be the best testosterone booster for men. These include testosterone pills, testosterone tablets, and otc testosterone options. While their ingredients vary—often featuring herbs like ashwagandha, fenugreek, or D-aspartic acid—their absorption and efficacy are influenced by hydration status.
Water is essential for the breakdown and assimilation of oral supplements. Without sufficient fluid intake, bioavailability may be compromised, reducing the effectiveness of testosterone boosters. Moreover, some test booster formulas include diuretics or caffeine, which can increase fluid loss and potentially exacerbate dehydration if not managed carefully.
Thus, anyone considering over the counter testosterone should prioritize water intake to optimize outcomes. Whether you’re wondering, “do testosterone pills work?” or “do testosterone boosters work?”, the answer may hinge partly on hydration. Supporting supplement protocols with proper fluid balance creates the internal conditions necessary for hormonal optimization.
Quick vs. Long-Term Hormonal Gains: How to Increase Testosterone Levels Quickly
Many individuals seek fast results and search for how to increase testosterone levels quickly. While there are strategies that can yield short-term hormonal boosts—such as intense resistance training, short-term caloric surpluses, or strategic supplementation—hydration remains a foundational factor that supports both immediate and sustained gains.
Acute dehydration can cause a rapid decline in testosterone, especially in high-stress or high-performance environments. Conversely, correcting dehydration quickly can help restore hormonal equilibrium. For those seeking fast results, hydration can act as a catalyst when combined with testosterone boosters, high-protein meals, or red meat-based diets.
However, long-term strategies are essential for sustainable testosterone optimization. These include improving sleep quality, reducing chronic stress, engaging in strength training, and following a nutrient-rich diet. Water supports each of these efforts by aiding recovery, improving circulation, and ensuring metabolic efficiency. Whether your goal is how to gain testosterone or how to raise testosterone over time, consistent hydration is non-negotiable.

Global Trends: Testosterone Decline and the Role of Modern Lifestyle Factors
Testosterone levels in men have been declining globally over the past few decades, attributed to factors like stress, poor diet, sedentary lifestyles, and environmental toxins. Hydration is often left out of this discussion, despite its central role in nearly every metabolic and hormonal process.
Modern lifestyles characterized by chronic coffee consumption, processed foods, alcohol use, and screen exposure often lead to underhydration. Addressing this foundational need can enhance all other interventions aimed at how to naturally increase testosterone. Restoring hydration habits in conjunction with physical activity, nutrient-dense diets, and minimal exposure to endocrine disruptors can reverse some of the downward trends in hormonal health.
Biohacking and Nootropics: Crossroads of Hydration, Cognition, and Testosterone
In the biohacking community, there is growing interest in how hydration affects cognitive function and hormonal output simultaneously. Nootropics—substances that enhance brain performance—often interact with testosterone through shared metabolic pathways involving dopamine, acetylcholine, and serotonin.
Dehydration impairs cerebral blood flow, leading to brain fog and reduced motivation—symptoms often mistaken for low testosterone. By ensuring hydration, individuals can optimize neurotransmitter balance and energy production in tandem with testosterone support. This is particularly relevant for those using testosterone supplements for men in pursuit of both physical and mental enhancement.
Hydration Apps and Smart Technology: Personalized Water Tracking
The advent of wearable technology and hydration tracking apps has made it easier to monitor water intake in real time. Devices can now estimate sweat loss, calculate fluid needs based on environmental exposure, and provide reminders to drink water based on heart rate variability or skin temperature.
Such technology enhances awareness and consistency, particularly for individuals using testosterone pills or testosterone tablets that require timing and digestive coordination. Whether one is experimenting with the top testosterone booster or focusing on foods that boost testosterone, using smart tools can streamline the integration of hydration into daily health routines.
Integrating Adaptogens and Herbal Hydration for Hormonal Support
A lesser-explored yet valuable strategy involves using herbal teas and adaptogenic infusions as part of a hydration plan. Herbs like ashwagandha, maca root, ginseng, and nettle are known for their potential to support testosterone production. When steeped in hot water, they serve dual roles: promoting hydration and delivering bioactive compounds that modulate the HPG axis.
Herbal hydration supports adrenal resilience and reduces oxidative stress, which often interferes with testosterone balance. Additionally, certain adaptogens act as mild diuretics, so their use should be balanced with electrolyte replenishment. Including these options in one’s hydration routine allows for a more functional approach to both water intake and hormonal optimization.
Hydration for Athletes and Bodybuilders: Testosterone Preservation During Extreme Training
Athletes, especially bodybuilders, are often at higher risk for dehydration due to intense physical exertion and the use of performance-enhancing supplements. During extreme workouts, fluid loss through sweat can impair blood volume and reduce nutrient delivery to the testes and adrenal glands, blunting testosterone output.
Hydration strategies for athletes should include not just water but also carbohydrate-electrolyte solutions that maintain plasma osmolality and support glucose metabolism. These practices may help preserve testosterone during peak training periods. For those incorporating testosterone boosters or researching how to increase testosterone levels quickly, hydration becomes a critical performance enhancer, not just a recovery aid.
Endocrine Disruptors, Water Quality, and Testosterone Suppression
Another hidden factor is water quality. Contaminants like bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and heavy metals in drinking water can function as endocrine disruptors. These chemicals mimic hormones or interfere with receptor binding, potentially leading to suppressed testosterone production over time.
Filtering drinking water through activated carbon or reverse osmosis systems may help reduce exposure to these harmful compounds. Choosing BPA-free water bottles and avoiding plastic containers exposed to heat can further minimize endocrine disruption. By improving both hydration quantity and quality, individuals take a two-pronged approach to hormonal health.
The Safety of Testosterone Supplements: Are Testosterone Boosters Safe?
Another frequently asked question is: are testosterone boosters safe? The answer depends on the quality of the product, individual health status, and usage patterns. Reputable supplements that contain well-studied ingredients are generally considered safe when taken as directed. However, safety also hinges on maintaining hydration to prevent adverse reactions.
Dehydration can amplify side effects like dizziness, headaches, or gastrointestinal discomfort—especially with concentrated herbal extracts. Ensuring adequate fluid intake helps mitigate these risks and supports the proper breakdown and elimination of supplement components.
Furthermore, some testosterone supplements for men include ingredients that stimulate diuresis, increasing the need for hydration. Monitoring water intake while using such products can enhance safety and efficacy. Whether exploring otc testosterone options or testosterone pills for men, water remains an essential co-factor in maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): The Surprising Link Between Hydration and Testosterone
1. Can dehydration mimic low testosterone symptoms?
Yes, chronic dehydration can produce symptoms that overlap significantly with low testosterone, such as fatigue, mood instability, muscle weakness, and reduced libido. These symptoms arise because dehydration can impair cellular energy production and reduce blood volume, which directly affects oxygen and nutrient delivery. Over time, the body’s ability to regulate hormones through the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis may also be compromised. This makes it difficult to distinguish between low testosterone and simple underhydration without proper testing. Ensuring optimal hydration can help differentiate between the two and potentially alleviate symptoms before turning to testosterone boosters or supplements.
2. How does hydration impact the absorption of testosterone pills?
Hydration plays a surprisingly critical role in how efficiently the body absorbs oral supplements, including testosterone pills for men. Water supports gastric motility and ensures that the supplement dissolves properly in the stomach, allowing for maximum nutrient uptake. Dehydration can slow digestion, reduce blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, and hinder enzymatic activity, all of which lower the bioavailability of testosterone supplements. Additionally, if someone is using over the counter testosterone, drinking adequate water throughout the day ensures the supplement’s active ingredients are effectively transported and metabolized. This simple habit can make the difference between a supplement working as intended or being minimally effective.
3. Why do athletes need to pay special attention to hydration and testosterone?
Athletes often underestimate the hormonal toll of dehydration during intense training. When fluid levels drop, cortisol increases to compensate for physical stress, which can suppress testosterone production. Maintaining hydration during high-intensity exercise helps preserve blood volume, stabilize body temperature, and limit hormonal dysregulation. This becomes particularly important when athletes are experimenting with the best testosterone booster for men or seeking ways for how to increase testosterone levels quickly. Proper hydration acts as a buffer against exercise-induced testosterone decline, supporting endurance, strength, and post-training recovery.
4. Does drinking water increase testosterone better when paired with certain foods?
Interestingly, the effect of hydration on testosterone may be amplified when combined with testosterone-friendly nutrition. Foods that increase testosterone, such as tuna, eggs, spinach, and Brazil nuts, rely on sufficient hydration to be properly digested and their nutrients absorbed. For instance, zinc and magnesium—two minerals critical for testosterone production—require water for optimal transport and utilization in cells. Therefore, a combination of water intake and a diet rich in foods that boost testosterone creates a synergistic effect. Even those using testosterone boosters can benefit from this nutritional-hydration pairing to optimize hormonal outcomes.
5. Does Drinking Water Increase Testosterone More in Certain Climates?
Yes, climate and environment can influence how hydration affects testosterone. In hot, humid conditions, sweat loss accelerates, and even mild dehydration can lead to increased cortisol levels and impaired endocrine function. Individuals in arid or tropical regions should be especially vigilant, as water loss can go unnoticed until symptoms manifest. Cold weather can also trick people into underhydrating, which has subtle but lasting hormonal effects. Whether you’re researching how to raise testosterone or evaluating testosterone supplements for men, climate-specific hydration strategies can enhance effectiveness and hormonal stability.
6. Are Testosterone Boosters Safe to Use During Dehydration?
While some may wonder, “are testosterone boosters safe?” under normal conditions, using them while dehydrated can be risky. Dehydration increases the concentration of substances in the blood, which can intensify the physiological effects of certain ingredients in testosterone boosters. For example, caffeine-based test booster products can cause jitters, anxiety, or palpitations when fluid levels are too low. Herbal extracts like tribulus terrestris and fenugreek may also have stronger effects or side effects without adequate water. It’s crucial to hydrate properly when taking testosterone pills or any testosterone booster for man to ensure both safety and effectiveness.
7. Does protein boost testosterone differently depending on hydration?
Protein intake is essential for hormonal support, especially in physically active individuals aiming for how to gain testosterone. However, the body’s ability to process and utilize protein efficiently depends on hydration. Dehydrated states impair kidney function, limiting the clearance of protein byproducts such as urea and ammonia. This can lead to muscle fatigue, stress on organs, and even hormone suppression over time. When asking, “does protein boost testosterone?” it’s worth noting that water is necessary to facilitate protein metabolism, making hydration a critical partner in protein-focused testosterone strategies.
8. Can I take testosterone while following a high-hydration regimen?
Absolutely, and in fact, pairing testosterone therapy or supplementation with a high-hydration approach is often recommended. Hydration can support the liver and kidneys in metabolizing exogenous testosterone while minimizing adverse effects. Additionally, those asking “can I take testosterone?” should consider their hydration habits as part of their readiness. High fluid intake supports cardiovascular health, reduces the risk of thickened blood (a side effect of testosterone therapy), and helps the body adapt to hormonal shifts. Whether you’re on prescribed testosterone or using otc testosterone, staying hydrated amplifies results while minimizing risk.
9. Does Drinking Water Increase Testosterone in Women Differently?
When asking “does drinking water increase testosterone” in women, it’s important to recognize hormonal complexity. Women produce testosterone in smaller amounts, but it plays a key role in mood, metabolism, and bone health. Hydration influences female hormone balance by affecting adrenal function and menstrual cycle regularity. For women exploring how to increase testosterone in females naturally, hydration acts as a foundational support for lifestyle and dietary interventions. It can also help regulate symptoms related to hormonal fluctuations during menopause or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), further enhancing quality of life.
10. How do testosterone tablets compare to testosterone boosters in terms of hydration needs?
While testosterone tablets and testosterone boosters both aim to raise hormonal levels, they differ significantly in formulation and metabolic demand. Tablets, especially prescription-based, often require liver processing, placing greater strain on detoxification pathways that rely on hydration. Testosterone boosters, on the other hand, typically use herbal or amino acid-based compounds to stimulate natural hormone production. Regardless of the route, both forms need optimal hydration for maximum effectiveness. In fact, many testosterone tablets review entries overlook this critical element, yet it’s a key variable in absorption, tolerability, and hormonal response. Integrating hydration into both approaches enhances long-term outcomes for anyone seeking how to naturally increase testosterone or boost levels safely.
Conclusion: The Vital Link Between Hydration and Testosterone Health
In a world flooded with advice on how to increase testosterone, one simple yet powerful strategy is often overlooked: hydration. While the question “does drinking water increase testosterone?” may not yield a straightforward yes or no, the evidence suggests that water plays an indispensable role in supporting hormonal balance. From reducing cortisol and improving nutrient absorption to enhancing the efficacy of testosterone boosters and supplements, hydration forms the foundation of endocrine health.
Whether you are an athlete, a health enthusiast, or someone exploring how to increase free testosterone or how to increase testosterone in females naturally, prioritizing hydration is a science-backed, low-risk, and highly effective approach. In combination with testosterone-friendly nutrition, supplements, and lifestyle practices, drinking water becomes more than a habit—it becomes a transformative strategy for achieving optimal hormonal health.
So the next time you reach for a glass of water, remember: you’re not just quenching your thirst; you may be supporting your testosterone levels and contributing to your overall vitality. As part of a comprehensive strategy involving the best testosterone booster for men, foods that increase testosterone, and a commitment to well-being, hydration emerges as a powerful, natural ally in the pursuit of hormonal health.
Further Reading:
The Best Testosterone Boosters for Men Over 50