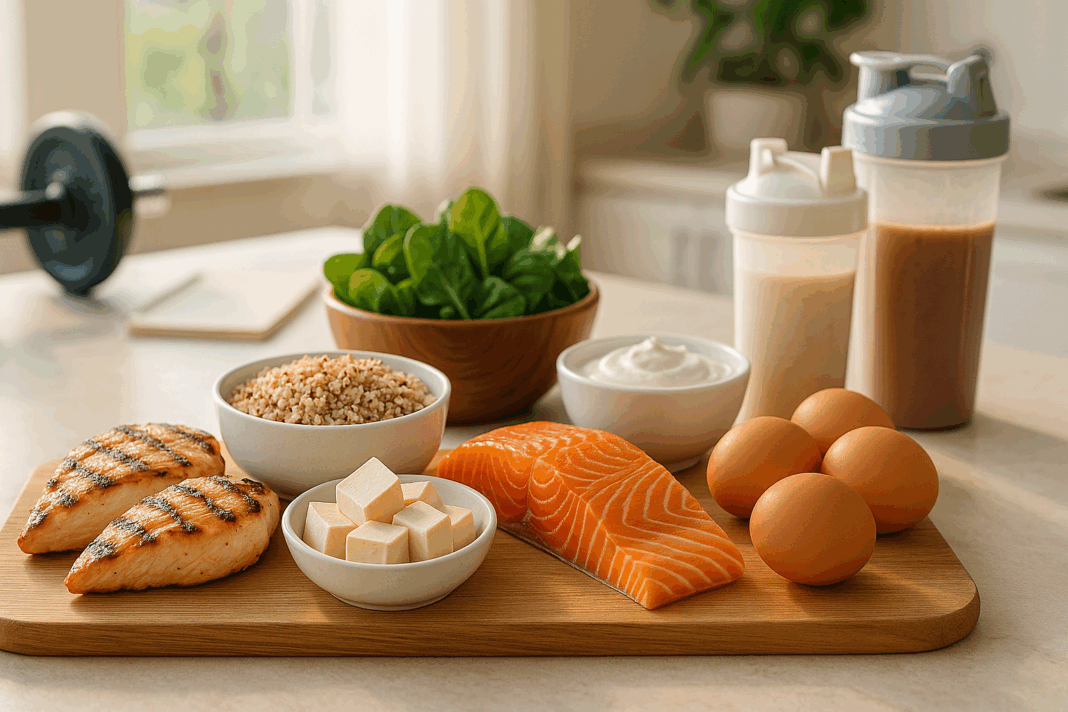
The intersection of fat loss and muscle building is a nutritional puzzle that many attempt to solve without fully understanding the science behind it. Creating a meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain requires much more than simply eating less or lifting more. It demands strategic integration of macronutrient timing, caloric control, and evidence-based protein optimization. The modern approach to body recomposition is deeply rooted in peer-reviewed studies that highlight the power of protein to stimulate muscle protein synthesis while simultaneously preserving lean tissue during calorie deficits. In this article, we unpack the science behind the high-protein diet and deliver a comprehensive, practical blueprint that serves as your ultimate meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain. This is not a crash course in dieting, but a sustainable and physiological pathway toward reshaping your body composition.
You may also like : The Ultimate High-Protein Nutrition Plan: How to Gain Muscle in Women Safely and Effectively
Why Protein Is the Cornerstone of Transformation?
Protein is far more than a muscle-building nutrient. Its thermogenic properties make it essential for those aiming to shed fat while preserving or building lean mass. Scientific literature consistently underscores that higher-protein diets result in greater fat loss and more significant muscle preservation compared to lower-protein counterparts. Protein’s high satiety index also curbs overeating, an essential component for maintaining a calorie deficit without psychological distress. From leucine-triggered muscle protein synthesis to insulin modulation and improved glucose metabolism, the physiological effects of protein go well beyond aesthetics.
Studies published in journals such as The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition and The Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition have shown that protein intake between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight is optimal for maximizing muscle gain while minimizing fat accumulation. When incorporated into a structured eating schedule for gaining muscle, protein creates the metabolic environment necessary for continuous anabolism and efficient recovery. It’s not surprising that every effective fat burning and muscle building diet begins with a high-protein foundation.
Understanding the Science of Body Recomposition
Body recomposition—the process of losing fat while gaining muscle—requires strategic manipulation of both energy balance and macronutrient distribution. Traditional diet culture often separates weight loss and muscle gain into two distinct phases, but recent studies have shown that with the right approach, both goals can be achieved simultaneously. A critical insight here is nutrient timing. Eating protein-rich meals evenly spaced throughout the day has been shown to stimulate muscle protein synthesis more effectively than large, sporadic protein intakes.
Hormonal regulation also plays a central role. High-protein intake stabilizes blood glucose levels, promotes satiety via GLP-1 and PYY release, and supports fat oxidation while minimizing muscle catabolism. Importantly, resistance training paired with a muscle gain diet plan further amplifies these effects by increasing the sensitivity of muscle tissue to amino acid uptake. This is where combining a meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain with targeted strength training becomes a game-changing strategy.
The best way to lose fat and gain muscle is not by extreme caloric deficits or protein megadoses but through a fine-tuned balance that meets your body’s energy needs while driving adaptive responses in muscle tissue. This requires a deliberate calorie distribution, ideally with slight deficits or surpluses tailored around workout days, and a consistent muscle building diet plan that evolves with progress.

The Meal Plan for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain: Daily Structure
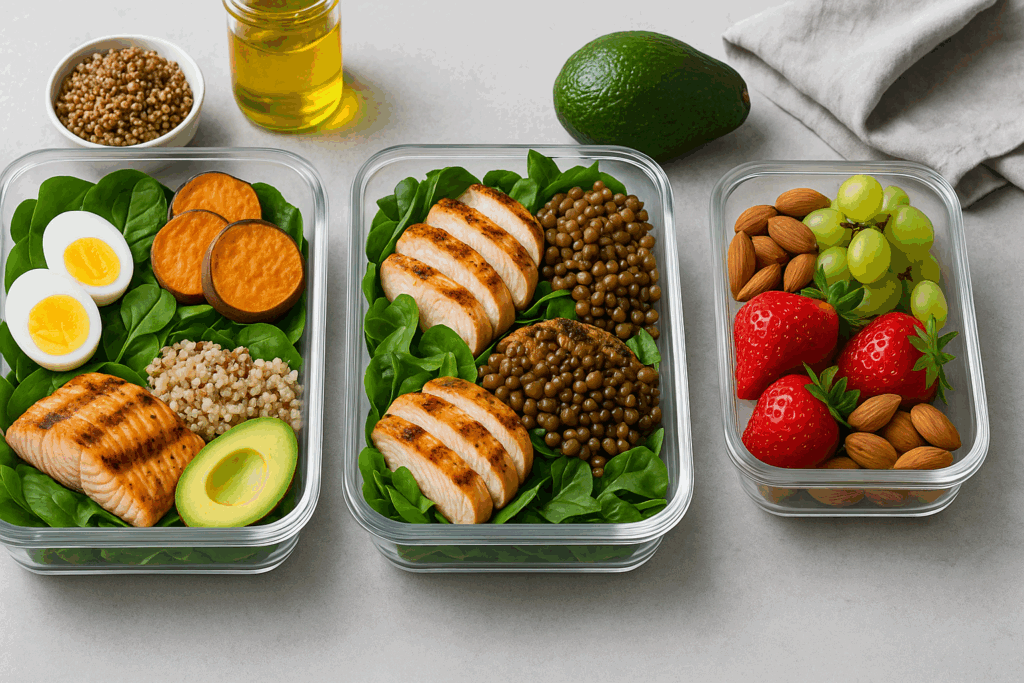
To implement a sustainable and effective meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain, structure is essential. A consistent eating schedule for gaining muscle should include three primary meals and two high-protein snacks. This pattern supports a steady stream of amino acids, stabilizes insulin, and prevents muscle breakdown.
Each meal should contain a high-quality protein source such as lean meats, eggs, Greek yogurt, or plant-based proteins like lentils and tempeh. Carbohydrates should be selected based on glycemic index and fiber content, favoring oats, sweet potatoes, quinoa, and legumes to provide sustained energy and micronutrient density. Fats should include essential fatty acids from sources like avocado, olive oil, and fatty fish, which support hormonal health and reduce systemic inflammation.
The goal is not to create rigid food rules but to establish a rhythmic dietary approach that becomes second nature. This consistency helps the body recognize feeding patterns, optimize digestion, and enhance nutrient absorption—all essential in the execution of a muscle growth diet plan. The fat-burning component is activated through slight caloric deficits and strategic carb cycling, ensuring that muscle mass is maintained even as fat stores are reduced.
Morning Fuel: Optimizing Breakfast for Muscle Protein Synthesis
Breakfast is often misunderstood or skipped, yet it is pivotal in a high-protein meal plan designed for weight loss and muscle gain. After an overnight fast, the body is in a catabolic state, and failing to break this fast with quality nutrients may hinder muscle recovery and increase muscle protein breakdown. A balanced breakfast that includes around 30-40 grams of protein can effectively kickstart muscle protein synthesis.
Eggs, turkey bacon, protein smoothies with whey or plant-based protein, Greek yogurt with chia seeds, or tofu scrambles are excellent options. Including moderate carbs like oatmeal or berries provides glycogen replenishment and sustained energy, while a touch of healthy fat from nuts or flaxseed rounds out the meal.
The inclusion of a high-protein breakfast also has downstream effects on hunger regulation. Studies show that individuals who consume protein-rich breakfasts report fewer cravings throughout the day and have better insulin sensitivity, which is particularly beneficial for those combining a diet to build muscle and lose fat. The result is a morning meal that fuels the body, primes it for training, and sets the metabolic tone for the day.
Midday Mastery: Lunch That Supports Fat Loss and Muscle Maintenance
Lunch is a crucial opportunity to reinforce the body’s anabolic state while keeping caloric intake controlled. This meal should anchor the day’s macronutrient goals and provide a robust amount of protein to combat the afternoon muscle breakdown that often accompanies extended fasting periods between meals. A common mistake among those new to the muscle gain diet plan is under-eating at lunch, which can trigger metabolic slowdown and subsequent overeating at dinner.
Grilled chicken breast, salmon, lean beef, or plant-based alternatives like lentils and quinoa can be combined with fibrous vegetables and slow-digesting carbohydrates to create a thermogenic, muscle-supporting meal. Including healthy fats from avocado or olive oil can improve nutrient absorption and help regulate inflammation.
This meal is also an ideal time to introduce strategic carbohydrate cycling. On training days, slightly increase the intake of starchy carbs to replenish glycogen and fuel performance. On rest days, keep carbs lower while maintaining protein to preserve lean tissue. This approach helps reduce fat and build muscle simultaneously by aligning nutrition with physical output, a cornerstone of any effective meal prep for muscle gain.
Evening Excellence: High-Protein Dinners That Promote Recovery
Dinner often marks the final opportunity of the day to meet protein requirements and prepare the body for overnight recovery. During sleep, the body undergoes significant repair, and ensuring a high-protein, low-glycemic dinner supports muscle growth while minimizing fat accumulation. A meal rich in casein or slow-digesting proteins provides a steady release of amino acids throughout the night, a strategy supported by emerging research in muscle physiology.
A typical high-protein dinner might include grilled turkey, baked cod, or a plant-based lentil stew, paired with roasted vegetables and a complex carbohydrate like farro or brown rice. Including a healthy fat source, such as tahini or coconut oil, supports hormonal balance and satiety. Seasonings like turmeric, ginger, and black pepper can also add anti-inflammatory benefits, supporting muscle recovery and gut health.
Those following a diet to lose weight and gain muscle should avoid late-night snacking on high-sugar items, which can spike insulin and interfere with growth hormone release. Instead, a small, protein-rich evening snack like cottage cheese or a casein shake before bed can further extend the anabolic window and support muscle protein synthesis overnight.
The Science of Snacking: Protein-Rich Mini Meals for Sustained Gains
Snacking has a bad reputation in many diet circles, but when executed properly, it can be a powerful tool for muscle building and fat loss. In a 7 day meal plan for muscle gain and fat loss, snacks serve as micro-opportunities to fuel the body between larger meals, maintain stable energy levels, and reinforce amino acid availability for continuous muscle protein synthesis.
High-protein snack ideas include hard-boiled eggs, beef jerky, edamame, protein bars, or cottage cheese with berries. The key is to keep these snacks under 250 calories while aiming for 15-25 grams of protein. This helps prevent overeating while ensuring that the muscle-building engine stays ignited throughout the day.
For those seeking the best way to lose fat and gain muscle, structured snacks prevent catabolic gaps that can lead to muscle degradation. Research indicates that evenly spaced protein intake, approximately every 3-4 hours, optimizes anabolism and improves recovery, especially for those training intensely or pursuing a diet plan to gain muscle mass.
Meal Timing and Circadian Rhythms: When You Eat Matters
Emerging research in chrononutrition suggests that the timing of meals plays a significant role in metabolic health and body composition. Eating the majority of calories earlier in the day, aligned with the body’s circadian rhythm, can improve insulin sensitivity and support fat oxidation. This approach complements a high-protein meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain by reinforcing hormonal balance and reducing the likelihood of nighttime overeating.
Intermittent fasting protocols, such as time-restricted eating (TRE), have gained popularity and can be integrated into a muscle growth diet plan. However, these should be adjusted to ensure adequate protein distribution and calorie intake within the eating window. For example, an 8-hour feeding window from 10 a.m. to 6 p.m. can still accommodate three meals and two snacks if planned strategically.
Ultimately, the timing of protein intake—particularly around workouts—is critical. Consuming a high-protein meal or shake within two hours post-exercise enhances muscle protein synthesis and accelerates recovery. This strategic alignment of nutrient timing with training intensity is a defining feature of any successful fat burning and muscle building diet.
The 7 Day Meal Plan for Muscle Gain and Fat Loss: A Practical Guide
Creating a sustainable and effective 7 day meal plan for muscle gain and fat loss requires a balance of science and flexibility. Begin by calculating your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE) and applying a modest caloric deficit of 10-15% for fat loss or a similar surplus for muscle gain. Adjust macronutrient targets to reflect a protein intake of 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight, moderate fats, and carbs tailored to your training schedule.
Each day should include breakfast, lunch, dinner, and two snacks, all centered around high-quality proteins. Rotate between animal and plant-based protein sources to ensure micronutrient variety. Use Sunday as a meal prep day to portion out meals and reduce decision fatigue throughout the week. This organization promotes consistency, a non-negotiable factor in achieving a lean, muscular physique.
A sample day on a muscle gain diet plan might include scrambled eggs with spinach and oats for breakfast, grilled chicken and quinoa salad for lunch, salmon with sweet potatoes and broccoli for dinner, and snacks like Greek yogurt or a protein smoothie. This structure can be modified based on dietary preferences, allergies, and specific goals but should always maintain the foundational principles of a diet to lose fat and gain muscle.
Social and Cultural Influences on Dietary Habits
A successful meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain must navigate real-world social and cultural contexts. Family traditions, religious dietary restrictions, work schedules, and social eating environments all influence how well individuals adhere to a plan.
Cultural dietary staples, such as rice in Asian diets or legumes in Mediterranean and South American cuisines, can be seamlessly integrated into high-protein meal plans. Understanding the role of food in cultural identity allows for more inclusive meal planning that doesn’t feel restrictive or isolating.
Meal prepping and batch cooking can offer practical solutions for busy professionals or families, making it easier to adhere to a structured plan. Providing room for flexibility and cultural adaptation in a muscle gain diet plan not only improves adherence but also enriches the culinary experience, making the journey both practical and pleasurable.
Nutrient Density vs. Caloric Density: Choosing Quality Over Quantity
A recurring challenge in designing a muscle gain diet plan is balancing nutrient density with caloric requirements. Nutrient-dense foods provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants with relatively low calories, while calorically dense foods pack more energy with fewer micronutrients.
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods ensures that a calorie-controlled diet doesn’t lead to deficiencies or suboptimal health. Foods like leafy greens, colorful vegetables, fatty fish, eggs, and berries should be dietary staples regardless of caloric goals. Conversely, highly processed foods, even those labeled “high-protein,” often contain additives, excessive sodium, and unhealthy fats that undermine metabolic and cardiovascular health.
Emphasizing whole foods in a muscle growth diet plan supports energy levels, reduces inflammation, and enhances recovery. This principle becomes especially important during cutting phases or when executing a 7 day meal plan for muscle gain and fat loss where food volume is reduced. Maximizing the nutrient impact of each calorie consumed is key to long-term adherence and success.
Precision Nutrition: Tailoring Meal Plans to Genetic and Metabolic Profiles
While generalized advice offers a solid foundation, individual responses to high-protein diets vary widely due to genetic and metabolic differences. Precision nutrition seeks to tailor dietary strategies to an individual’s genomic, microbiomic, and metabolic makeup, offering a more personalized approach to achieving a lean, muscular physique.
Genetic markers such as FTO, PPARG, and ACTN3 can influence responses to macronutrients, fat metabolism, and muscle fiber type distribution. Some individuals may respond better to higher fat intakes with moderate protein, while others may thrive on a high-carb, high-protein combination. Metabolic testing, such as resting metabolic rate (RMR) or respiratory quotient (RQ), can also refine caloric needs and macronutrient balance.
This individualized approach enhances the efficacy of a fat burning and muscle building diet by aligning it with the body’s unique physiology. With the rise of DNA-based nutrition services and wearable technology, customizing a 7 day meal plan for muscle gain and fat loss is no longer reserved for elite athletes but is increasingly accessible to anyone seeking optimal results.
The Gut-Muscle Axis: How Digestive Health Affects Body Composition
Recent research has introduced the concept of the gut-muscle axis, which explores how the health of the digestive system impacts muscle growth, fat loss, and overall metabolic health. A balanced gut microbiome enhances nutrient absorption, reduces inflammation, and supports hormonal regulation—all essential in a muscle building meal plan.
High-protein diets, particularly those high in animal protein, can alter the gut microbiota composition. While this isn’t necessarily harmful, it does emphasize the importance of fiber, polyphenols, and fermented foods in preserving gut diversity and function. Including fibrous vegetables, legumes, and probiotics like kefir or kimchi can prevent dysbiosis and optimize digestion.
An efficient gut can improve the assimilation of amino acids, boost immunity, and regulate energy production. In the context of a diet to build muscle and lose fat, this translates to more effective use of consumed nutrients and less systemic inflammation—an ideal environment for cellular repair and lean mass accrual.
Hydration, Supplementation, and Recovery: Beyond the Plate
Nutrition is only one pillar of transformation. Hydration plays a critical role in cellular function, nutrient transport, and metabolic health. Aim for at least 3 liters of water per day, adjusting based on training volume and climate. Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium should also be monitored, especially for those engaging in high-volume resistance or endurance training.
Supplementation can support, but not replace, a whole-food-based meal program to gain muscle. Evidence-based supplements include whey or plant-based protein powders, creatine monohydrate, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D3. These additions can enhance muscle protein synthesis, reduce inflammation, and improve recovery timelines.
Equally important is recovery. Quality sleep (7-9 hours per night), regular mobility work, and periodized training schedules ensure that the gains made through a high-protein diet are not undone by stress or overtraining. When all these factors align, the synergy between diet, exercise, and recovery creates the optimal environment for reducing fat and building muscle sustainably.
Frequently Asked Questions: Advanced Insights Into Your High-Protein Transformation
1. What Makes a Meal Plan for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain More Effective Than Standard Diets?
A meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain surpasses generic dieting because it balances the unique metabolic demands of muscle tissue with the caloric precision needed for fat reduction. Muscle is metabolically active, meaning it burns more calories at rest compared to fat, and thus requires consistent protein intake for preservation and growth. Unlike traditional low-fat or low-calorie diets, this approach uses strategic macronutrient manipulation to maintain muscle even during calorie deficits. Timing and variety also play crucial roles; rotating protein sources and aligning intake with training periods amplifies both muscle recovery and fat mobilization. Moreover, this dual-focused strategy supports long-term sustainability, allowing for goal adjustment over time without derailing progress.
2. How Can I Sustain Long-Term Results With a 7 Day Meal Plan to Gain Muscle Mass?
The secret to lasting change lies in consistency and cyclical adaptation of your 7 day meal plan to gain muscle mass. Start by adjusting the plan based on your training volume, recovery rate, and energy expenditure—this ensures you’re not over- or underfeeding. Monitor not only your physical measurements but also your energy levels, digestion, and mental clarity to gauge effectiveness. After every few weeks, rotate your protein and carb sources to prevent dietary fatigue and ensure a broader nutrient spectrum. Most importantly, adopt a mindset that views your muscle building meal plan as a lifestyle rather than a temporary phase, which encourages continuous growth and adherence.
3. What Role Does Sleep Play in a Diet to Lose Weight and Gain Muscle?
Sleep is a powerful yet underappreciated ally in any diet to lose weight and gain muscle. During deep sleep cycles, growth hormone secretion peaks, enabling muscle recovery and fat mobilization. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt leptin and ghrelin levels, increasing hunger and reducing satiety, which undermines fat-burning efforts. Moreover, poor sleep impairs insulin sensitivity, making it harder for your body to partition nutrients efficiently. To maximize the effects of your high-protein meal plan, aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep, supported by a consistent bedtime routine and a sleep-friendly environment.
4. Can Women Use the Same Meal Plan Muscle Gain Fat Loss Strategies as Men?
Absolutely, but with slight modifications tailored to hormonal profiles and caloric needs. Women can follow a meal plan muscle gain fat loss regimen effectively by adjusting total calorie intake and prioritizing nutrient-dense foods that support hormonal health. For example, incorporating flaxseeds and fatty fish can help balance estrogen levels, while consistent protein intake stabilizes blood sugar. Additionally, strength training combined with a diet to build muscle and lose fat has shown equal benefits in women for improving lean mass and reducing body fat. Awareness of menstrual cycle phases can also enhance training and nutrition synchronization, optimizing results.
5. What to Eat to Lose Weight and Gain Muscle When You’re Plant-Based?
For plant-based athletes, the cornerstone of what to eat to lose weight and gain muscle includes diverse protein sources like lentils, tofu, tempeh, seitan, edamame, and quinoa. Supplementing with a high-quality plant-based protein powder ensures you meet daily protein goals critical for muscle repair and synthesis. Nutritional yeast, chia seeds, and spirulina can also provide unique micronutrients that support recovery. A well-planned 7 day muscle building meal plan for plant-based individuals focuses on protein pairing and meal timing to achieve similar anabolic results as omnivorous diets. Ensure you monitor vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 intake to maintain optimal performance and metabolic health.
6. How to Burn Fat and Build Muscle Simultaneously Without Hitting a Plateau?
To avoid plateaus while learning how to burn fat and build muscle, integrate progressive overload in training and manipulate your macronutrients cyclically. Use carbohydrate cycling—higher intake on training days, lower on rest days—to maintain insulin sensitivity while fueling workouts. Adjust your eating schedule for gaining muscle based on your body’s feedback, not rigid time slots. Include deload weeks and refeed days every few weeks to reset your metabolism and give your body a chance to recover. Finally, monitor stress levels; high cortisol can hinder fat loss and muscle gain, so incorporate recovery protocols like meditation or active stretching.
7. Is There a Best Way to Lose Fat and Gain Muscle When Training Twice a Day?
For individuals training twice daily, the best way to lose fat and gain muscle is to prioritize intra-workout and post-workout nutrition. A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) supplement during your workout can prevent muscle breakdown, while a fast-absorbing protein shake immediately after restores muscle glycogen and promotes recovery. On such an intense schedule, a 7 day meal plan for muscle gain and fat loss should include six well-balanced meals that supply steady amino acid availability. Focus on carbohydrate timing around training sessions for performance, and keep the rest of your meals lower in glycemic load to enhance fat oxidation. Hydration and sleep are equally crucial to buffer the increased physical stress and avoid hormonal burnout.
8. How to Customize a Meal Plan for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain With Limited Time?
For busy professionals or parents, the key to customizing a meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain is effective meal prep for muscle gain. Batch-cooking lean proteins, freezing individual servings, and relying on portable high-protein snacks can streamline execution. Use slow cookers, pressure cookers, or air fryers to reduce cooking time while maintaining nutrient integrity. Incorporate versatile ingredients like canned beans, pre-washed greens, and whole grain wraps that can be assembled quickly into complete meals. Also, consider preparing a flexible muscle gain diet plan 7 days ahead with interchangeable parts to allow variety without complicating logistics.
9. What Emerging Trends Are Shaping the Future of the Muscle Growth Diet Plan?
The future of the muscle growth diet plan lies in personalized nutrition, microbiome analysis, and wearable tracking technology. Companies now offer DNA-based insights that tailor macronutrient ratios to your genetic profile, allowing for more precise diet adjustments. Gut health testing is also being used to recommend probiotic-rich foods that enhance nutrient absorption and reduce inflammation—both critical for muscle recovery. Meanwhile, smartwatches and glucose monitors provide real-time feedback that can guide meal timing and composition for optimal metabolic response. These innovations, when integrated with a classic muscle building diet plan, can significantly enhance individual outcomes and long-term success.
10. Can a 7 Day Meal Plan to Gain Muscle Mass Be Repeated or Does It Need Variation?
A 7 day meal plan to gain muscle mass can be repeated for up to four to six weeks, but incorporating variation enhances both physiological response and psychological adherence. Rotating protein sources—such as switching between turkey, tempeh, and salmon—ensures a full spectrum of amino acids and micronutrients. Additionally, changing carb and fat sources helps reduce dietary monotony and supports gut health. Consider seasonal produce or themed weeks (e.g., Mediterranean, Asian fusion) to keep meals exciting. Ultimately, the best meal program to gain muscle is one that evolves with your progress, adapts to your preferences, and maintains high nutritional integrity over time.
Conclusion : A Science-Based Blueprint for Lasting Transformation
Building the ideal physique is not about gimmicks, starvation, or fad diets—it is about consistency, structure, and evidence-based decisions. A thoughtfully constructed meal plan for weight loss and muscle gain, when aligned with your training, lifestyle, and physiological needs, can deliver sustainable results without extremes. Through understanding the science of protein metabolism, circadian nutrition, and muscle physiology, you gain the tools necessary to take control of your body composition.
Whether you follow a 7 day meal plan to gain muscle mass or craft your own meal prep for muscle gain, the principles remain the same: prioritize high-quality protein, align meals with your daily energy demands, and maintain a recovery-first mindset. In doing so, you not only reshape your body but also redefine your relationship with food, fitness, and long-term health. Let this guide be your roadmap to a leaner, stronger, and more resilient version of yourself—grounded in science, empowered by practice, and designed for real-life results.
Further Reading:
7-Day Bodybuilding Meal Plan: Foods to Eat & Avoid for Muscle Gain