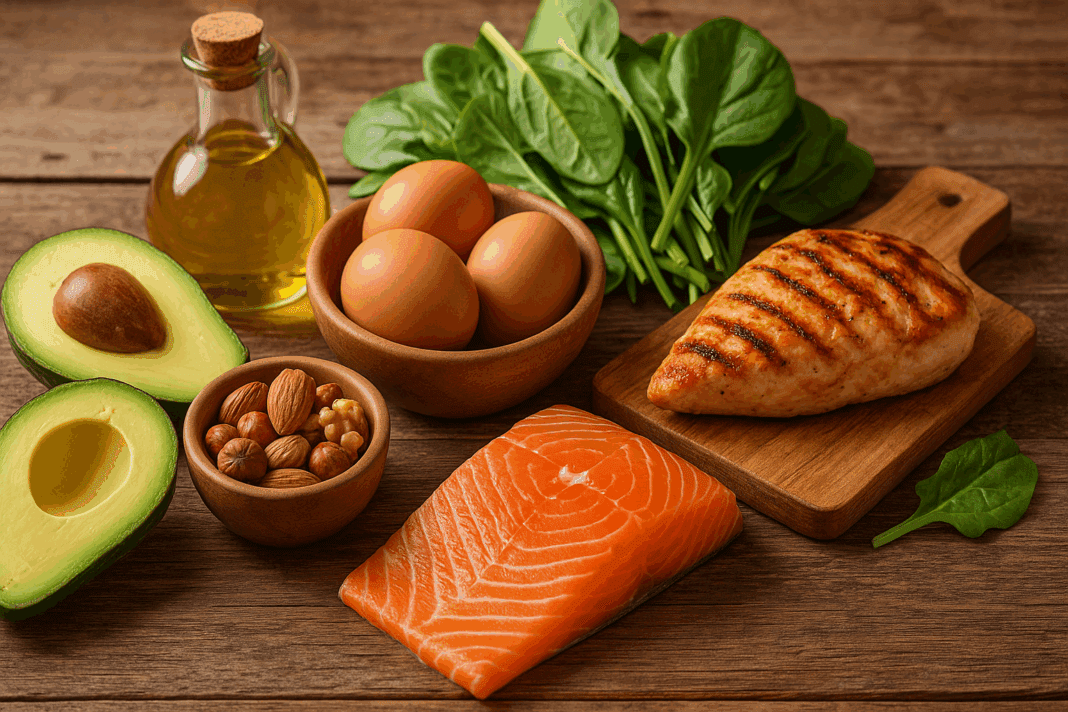
In today’s era of refined dietary science and personalized nutrition, one dietary trend has steadily gained credibility not just among fitness enthusiasts but also in clinical nutrition circles: the low carb LCHF approach. Low carb LCHF, which stands for low carbohydrate, high fat, offers a compelling alternative to traditional dietary paradigms that often prioritize carbohydrate intake. This model encourages a nutrient-dense, protein-rich intake that supports metabolic efficiency, hormonal balance, and even long-term health outcomes. The fusion of high-protein foods with the metabolic advantages of a low carb LCHF diet provides a unique foundation for those seeking sustainable weight management, improved metabolic markers, and enhanced physical performance.
You may also like : The Ultimate Guide to Choosing a High Protein Diet Name That Fits Your Goals
Understanding the Principles of a Low Carb LCHF Diet
To appreciate the surprising benefits of low carb LCHF diets, it is crucial to understand their nutritional architecture. Unlike typical diets rich in bread, pasta, and sugar, the low carb LCHF model significantly limits carbohydrate intake to induce a state of nutritional ketosis—a process whereby the body shifts from burning glucose to burning fat for fuel. This metabolic shift triggers the production of ketone bodies, alternative energy molecules derived from fat. Simultaneously, the diet emphasizes high consumption of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, while protein sources are carefully moderated to avoid excessive gluconeogenesis, which can potentially disrupt ketosis.
While protein intake is not the central macronutrient in LCHF diets, its role remains paramount in the context of a high-protein nutritional strategy. This intersection allows individuals to retain lean muscle mass, regulate appetite through increased satiety, and promote thermogenesis—all essential elements for optimal health. Understanding these interrelated metabolic processes is key to appreciating how a low carb diet high fat diet supports longevity, energy levels, and overall vitality.
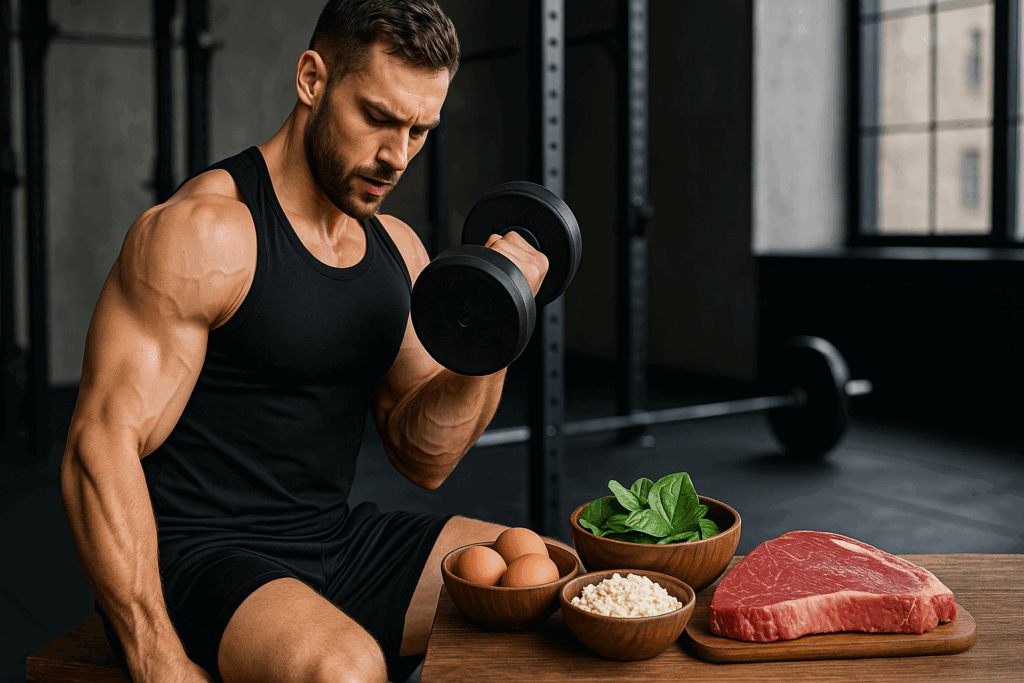

How Low Carb LCHF Diets Support Muscle Maintenance and Growth
Protein plays an essential role in building, maintaining, and repairing muscle tissues. For individuals following a low carb LCHF framework, protein becomes even more valuable due to its ability to preserve lean mass during fat loss phases. When carbohydrates are restricted, glycogen stores in muscles diminish, and the body relies on alternative fuel sources such as fat and ketones. During this adaptation phase, adequate protein intake ensures that the body does not catabolize muscle for energy.
Furthermore, consuming complete proteins from animal and plant-based sources contributes to the synthesis of all essential amino acids required for muscle recovery and growth. Low carb LCHF diets often include eggs, grass-fed beef, wild-caught salmon, and poultry, which are naturally high in bioavailable amino acids. When paired with resistance training or weight-bearing exercises, the diet fosters a metabolic environment conducive to muscle hypertrophy and maintenance, even when total caloric intake is slightly reduced.
Interestingly, recent studies suggest that individuals on a low carb diet high fat diet who consume moderate to high levels of protein may experience comparable—if not superior—muscle retention to those on high-carb regimens. This is due in part to the insulin-sparing effect of LCHF eating, which minimizes inflammation and enhances mitochondrial efficiency. Collectively, this points to the muscle-preserving advantages of integrating protein within a low carb LCHF protocol.
Low Carb LCHF Diets and Hormonal Balance: A Deeper Look
Hormonal regulation is an often-overlooked benefit of the low carb LCHF model, especially when paired with high-quality protein intake. Hormones such as insulin, leptin, ghrelin, cortisol, and testosterone play critical roles in body composition, appetite control, and energy homeostasis. The low carb lchf diet modulates these hormones in ways that support metabolic resilience and reduce the risk of chronic disease.
One of the most well-documented effects of carbohydrate restriction is the reduction in insulin levels. Persistently high insulin levels, often due to excessive carbohydrate consumption, can contribute to insulin resistance, weight gain, and eventually type 2 diabetes. By limiting carb intake and emphasizing fat and protein, a low carb LCHF diet stabilizes blood glucose and reduces insulin secretion, helping restore insulin sensitivity over time.
In addition to insulin, leptin and ghrelin—the hormones responsible for hunger and satiety—are more effectively regulated on an LCHF regimen. The satiating nature of dietary fat, combined with the thermic and filling effect of protein, reduces food cravings and spontaneous caloric intake. Moreover, a low carb LCHF dietary pattern may enhance testosterone levels in men and support progesterone balance in women by reducing body fat percentage, which in turn lowers estrogen dominance and improves hormonal equilibrium.
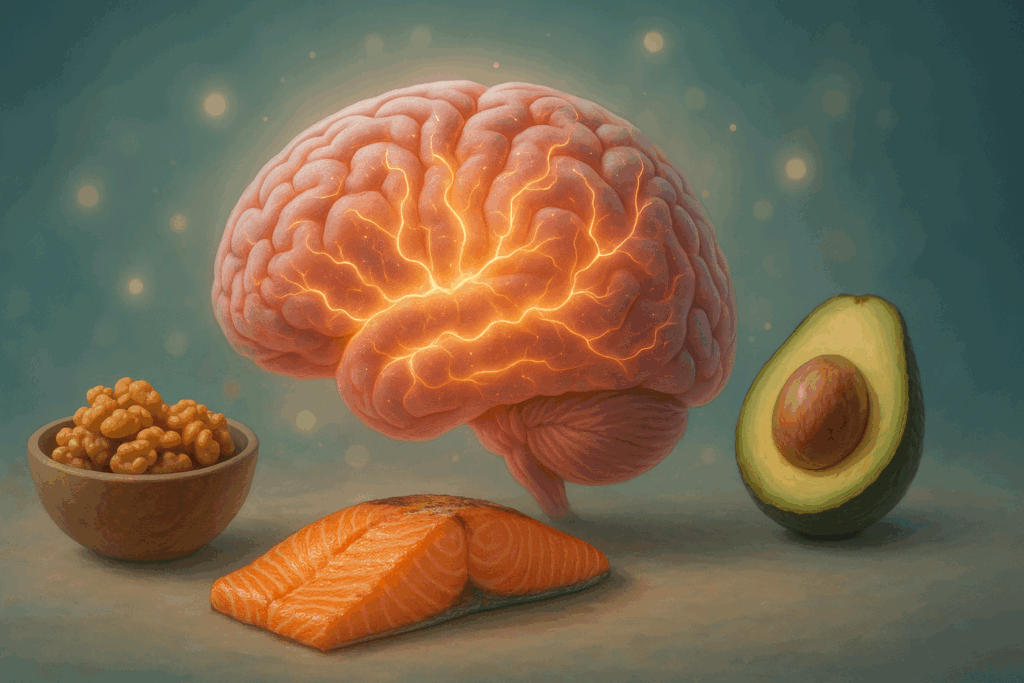

Improved Cognitive Performance Through Low Carb LCHF Nutrition
Cognitive health is another domain in which low carb LCHF protocols have shown promising results. The brain, while traditionally reliant on glucose for fuel, can adapt to use ketones as an efficient and stable energy source. This metabolic adaptation, often referred to as “ketoadaptation,” leads to enhanced mental clarity, sustained energy, and reduced cognitive fatigue.
For college-educated readers and professionals aiming to optimize mental acuity and focus, the low carb LCHF diet offers a dietary framework that supports neurogenesis, reduces neuroinflammation, and promotes mitochondrial efficiency in neurons. When carbohydrates are minimized, blood sugar fluctuations stabilize, resulting in fewer episodes of brain fog and reactive hypoglycemia. This provides a more consistent and reliable source of mental energy, particularly during extended periods of focus or stress.
Emerging research also highlights the neuroprotective benefits of ketones in delaying the onset and progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. While long-term studies are ongoing, preliminary evidence suggests that the metabolic shift induced by a low carb LCHF diet fosters an internal environment conducive to brain health and cognitive longevity.
The Role of a Low Carb Diet High Fat Diet in Weight Loss and Satiety
One of the most appealing and well-researched aspects of the low carb LCHF model is its efficacy in promoting weight loss without the need for extreme caloric restriction. The combination of satiety-inducing fats and thermogenic proteins naturally reduces appetite and promotes a spontaneous reduction in caloric intake. This allows for a more sustainable and psychologically rewarding dietary experience compared to conventional low-fat or calorie-restricted plans.
Weight loss on a low carb diet high fat diet is not solely a function of fewer calories but is largely influenced by hormonal changes. Reduced insulin levels promote lipolysis—the breakdown of stored body fat—while increased glucagon levels support the mobilization of fatty acids for energy. As ketone levels rise, appetite is further suppressed, resulting in greater adherence and reduced reliance on willpower alone.
Importantly, weight loss achieved on a low carb LCHF plan tends to prioritize fat loss over muscle loss. This is particularly beneficial for those seeking body recomposition, where the goal is to reduce fat mass while preserving or increasing lean mass. Combined with resistance training and adequate protein intake, the diet becomes a powerful tool for achieving and maintaining a healthy, sustainable body composition.

Metabolic Flexibility and the Low Carb LCHF Advantage
Metabolic flexibility refers to the body’s ability to efficiently switch between fuel sources based on availability and demand. In a typical high-carbohydrate diet, individuals become reliant on glucose as the primary energy source, often resulting in energy crashes when blood sugar levels dip. However, a low carb LCHF dietary approach trains the body to oxidize fat and utilize ketones as a primary energy source, even during fasting or low-intensity activities.
This metabolic adaptability enhances endurance, reduces fatigue, and supports overall vitality. Athletes and high-performers who adopt a low carb LCHF strategy often report improved stamina and quicker recovery times. Moreover, enhanced fat oxidation reduces the body’s dependency on frequent meals and snacks, allowing for greater meal flexibility and intermittent fasting compatibility.
The implications of improved metabolic flexibility extend beyond athletic performance. Individuals with metabolic syndrome, prediabetes, or insulin resistance can benefit from the stabilizing effects of a low carb diet high fat diet. Over time, consistent adherence retrains the body to become metabolically efficient, reducing the risk of lifestyle-related diseases and improving long-term health outcomes.

Low Carb LCHF Diets and Cardiovascular Health: Revisiting the Science
Historically, high-fat diets were vilified for their assumed link to heart disease. However, contemporary research paints a far more nuanced picture. A well-formulated low carb LCHF diet, rich in monounsaturated and omega-3 fats, may actually support cardiovascular health by improving lipid profiles and reducing inflammatory markers.
Contrary to outdated notions, studies reveal that LCHF diets can raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol, lower triglycerides, and shift LDL particles from small, dense (more atherogenic) to large, buoyant (less harmful) subtypes. These changes are strongly associated with reduced cardiovascular risk, particularly when coupled with weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity.
Furthermore, chronic inflammation—a key driver of atherosclerosis—is significantly reduced on a low carb LCHF diet. By minimizing refined sugars, processed grains, and industrial seed oils, individuals reduce exposure to pro-inflammatory foods and replace them with anti-inflammatory nutrients found in avocados, nuts, fatty fish, and olive oil. This anti-inflammatory effect, combined with the stabilizing impact on blood pressure and endothelial function, makes the low carb diet high fat diet a viable and potentially protective nutritional strategy for heart health.
Navigating Nutrient Density in a Low Carb LCHF Lifestyle
Despite misconceptions, a low carb LCHF approach can be rich in essential micronutrients when carefully curated. Whole-food-based LCHF meals often contain high levels of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, as well as minerals like magnesium, potassium, and zinc. Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, nuts, seeds, and organ meats provide a comprehensive nutritional profile that supports cellular function and physiological integrity.
In addition to micronutrients, phytonutrients and antioxidants are abundant in many low carb LCHF-compatible foods. For example, sulfur-containing compounds in garlic and onions support detoxification pathways, while polyphenols in olive oil and green tea reduce oxidative stress. These compounds work synergistically with dietary fats to enhance bioavailability and absorption, further amplifying the health-promoting effects of the diet.
The inclusion of diverse protein sources—including wild-caught fish, pasture-raised poultry, and grass-fed meats—ensures a complete amino acid spectrum and enhances nutrient density. Careful meal planning and rotation of food types can prevent nutrient monotony and reduce the risk of micronutrient deficiencies often associated with overly restrictive diets.

Adherence Psychology: Why Low Carb LCHF Works Long Term
One of the most underrated yet powerful elements of the low carb LCHF dietary strategy is its psychological impact on eating behavior. Traditional low-fat, calorie-restricted diets often rely on willpower, resulting in fluctuating motivation, persistent hunger, and eventual burnout. In contrast, the LCHF model works in harmony with satiety hormones, making it easier to sustain for the long term.
The combination of fat and protein significantly reduces ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger, while enhancing peptide YY and cholecystokinin, which promote satiety. This biochemical advantage translates into fewer cravings and reduced meal frequency, allowing individuals to transition naturally to fewer daily meals and even embrace intermittent fasting without distress.
Moreover, LCHF diets often eliminate highly palatable, hyper-processed foods that trigger addictive eating behaviors. By focusing on real, whole foods, individuals experience more regulated dopamine responses, fostering a healthier relationship with food. This shift in mindset reduces emotional eating, binge tendencies, and the guilt/shame cycle often associated with traditional dieting.

Sustainability and Practical Considerations for Daily Living
One of the key challenges in maintaining any dietary approach lies in its sustainability. Fortunately, the low carb LCHF model offers flexibility and satiety that make it more sustainable than many conventional diets. With an emphasis on whole foods, satisfying fats, and protein-rich meals, individuals are less likely to experience cravings, mood swings, or energy crashes that sabotage adherence.
Moreover, the diet’s compatibility with intermittent fasting, meal prepping, and intuitive eating adds practical value to everyday life. Busy professionals and parents can enjoy the simplicity of fewer meals per day without compromising on nutrition. Dining out, social events, and travel become manageable with some basic knowledge and preparation, such as choosing bunless burgers, grilled proteins, and low-carb vegetable sides.
Community support, recipe innovations, and the growing availability of low carb LCHF-friendly products further contribute to the diet’s long-term viability. When approached with balance and flexibility, the diet transforms from a temporary regimen into a lifestyle choice that fosters metabolic health, mental clarity, and physical resilience.
Athletic Performance: Rethinking Fuel Sources for Endurance
Conventional wisdom in sports nutrition has long emphasized carbohydrate loading and frequent glucose replenishment during exercise. However, a growing body of evidence suggests that fat-adapted athletes on low carb LCHF diets can perform at high levels of endurance without the need for constant carbohydrate intake.
By teaching the body to rely on fat and ketones for fuel, endurance athletes can access an almost limitless supply of energy, bypassing the glycogen depletion that leads to “bonking” or sudden fatigue. This is particularly advantageous in ultra-endurance events where refueling opportunities are limited, and digestive distress from carb-heavy gels and sports drinks is common.
While anaerobic or high-intensity performance may benefit from strategic carbohydrate cycling, many athletes find that they can maintain and even enhance their endurance capacity through consistent LCHF adherence. The reduction in inflammation and faster recovery times further support athletic resilience and long-term training outcomes.
LCHF and Blood Sugar Stability in Non-Diabetics
Although much of the research on low carb LCHF diets has focused on diabetic or prediabetic populations, non-diabetic individuals can also experience profound benefits in glycemic control. Stable blood sugar levels contribute to sustained energy, cognitive clarity, and improved mood.
In healthy individuals, large swings in blood sugar can still occur after consuming high-glycemic meals, leading to crashes, irritability, and increased hunger. The low carb LCHF model eliminates these fluctuations by minimizing the glycemic load of meals and enhancing insulin sensitivity over time. Even those with normal fasting glucose can benefit from reducing postprandial spikes and maintaining consistent energy levels throughout the day.
This is especially relevant for professionals, students, and high performers who rely on mental endurance and focus. Preventing blood sugar highs and lows allows for sustained concentration without the need for frequent snacking or caffeine dependence. Over time, this contributes to improved productivity, reduced stress, and greater emotional resilience.
The Environmental Footprint of LCHF Diets
As conversations around nutrition increasingly incorporate sustainability and environmental impact, the ecological implications of low carb LCHF diets warrant thoughtful examination. While critics often point to the carbon footprint of meat production, proponents of LCHF argue that sourcing food responsibly and emphasizing nutrient density can yield a more sustainable approach than one might initially assume.
Grass-fed, pasture-raised animals not only produce higher-quality protein and fats but also contribute to regenerative agriculture practices that enrich soil health, sequester carbon, and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers. When paired with seasonal, local vegetables and minimal food waste, the LCHF lifestyle can align with environmental stewardship principles.
Additionally, the focus on whole foods over ultra-processed options reduces reliance on industrial food systems, which are a major contributor to environmental degradation. By supporting ethical sourcing, reducing packaging waste, and embracing nose-to-tail consumption, LCHF followers can reduce their dietary footprint while enhancing personal health.
The Low Carb LCHF Blueprint for Long-Term Health
As the scientific understanding of nutrition evolves, so too does the appreciation for dietary frameworks like the low carb LCHF approach. Its integration of protein-rich foods with the metabolic benefits of carbohydrate restriction offers a blueprint for sustainable wellness, metabolic freedom, and vibrant living. Unlike fad diets that promise quick fixes, the low carb diet high fat diet is grounded in physiological principles that align with human metabolism, making it both effective and sustainable over the long haul.
Critically, the low carb LCHF model is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a versatile strategy that can be personalized based on age, activity level, health status, and personal preference. Whether the goal is fat loss, muscle gain, cognitive enhancement, or chronic disease prevention, the principles of the LCHF diet provide a flexible scaffold on which individuals can build their own nutrition plans.
With its solid foundation in nutritional science, its support for hormonal and metabolic balance, and its ability to foster long-term behavioral adherence, the low carb LCHF lifestyle is more than just a diet. It is a comprehensive nutritional philosophy that empowers individuals to take control of their health, optimize their physiology, and thrive across the lifespan.
Complementary Practices: Fasting, Sleep, and Stress Management
The benefits of a low carb LCHF diet can be amplified when integrated with complementary lifestyle practices such as intermittent fasting, sleep optimization, and stress reduction. Intermittent fasting, when paired with LCHF eating, accelerates fat adaptation and deepens ketone production, resulting in more profound metabolic benefits. Many find it easier to fast when fat and protein intake are optimized, as satiety is naturally prolonged.
Quality sleep is essential for metabolic regulation, immune function, and cognitive resilience. LCHF diets may support deeper sleep by stabilizing blood sugar and reducing nighttime awakenings caused by glucose crashes. Adequate magnesium and potassium, found in many LCHF-approved foods, also support muscle relaxation and nervous system balance.
Stress management practices such as mindfulness, nature exposure, and moderate exercise align well with the hormonal and metabolic improvements conferred by a low carb LCHF diet. Cortisol levels, which influence appetite, fat storage, and inflammation, are better regulated when blood sugar remains stable, and dietary stress is minimized. Together, these elements form a holistic lifestyle framework that supports total-body health.
Frequently Asked Questions: Deeper Insights into the Low Carb LCHF Lifestyle
1. What are some overlooked micronutrient considerations when following a low carb LCHF lifestyle?
While macronutrients take center stage in a low carb LCHF lifestyle, micronutrients can quietly make or break long-term success. Electrolytes such as magnesium, potassium, and sodium are often depleted during carbohydrate restriction, leading to fatigue, muscle cramps, and even heart palpitations. Another commonly overlooked issue is the reduction of vitamin C intake, since many LCHF adherents lower their consumption of fruits. Including low-carb vegetables like bell peppers and broccoli can help offset this. Additionally, selenium and iodine—critical for thyroid health—may be compromised when dairy or iodized salt is reduced. To maintain metabolic resilience, a strategic supplement plan or a micronutrient-dense food approach is essential.
2. How can individuals manage social situations while on a low carb LCHF or low carb diet high fat diet?
Sticking to a low carb diet high fat diet can feel socially isolating if you’re unprepared. Events often revolve around carb-heavy meals, making it difficult to maintain dietary consistency. One strategy is to eat beforehand, focusing on satiety-inducing fats and proteins, reducing the urge to indulge. Communicating your dietary preferences respectfully—without preaching—helps others accommodate you or at least understand your needs. Bringing your own LCHF-friendly dish to gatherings not only ensures you have something to eat but also introduces others to your lifestyle. With time, social integration becomes easier as you develop confidence in navigating menus, buffets, and well-meaning peer pressure.
3. Can the low carb LCHF approach be sustainable for athletes and physically active individuals?
Absolutely—but with strategic modification. Athletes can thrive on a low carb LCHF regimen, especially during endurance sports, where fat becomes a highly efficient fuel source. However, powerlifters and sprinters may initially experience reduced performance due to the glycogen demands of anaerobic activity. In such cases, targeted carbohydrate intake around workouts can optimize both performance and adherence to a low carb diet high fat diet. Additionally, consuming high-quality fats like MCT oil may further support energy levels. Over time, many athletes report enhanced metabolic flexibility, faster recovery, and reduced inflammation when incorporating LCHF principles appropriately.
4. What are the long-term psychological benefits of adopting a low carb LCHF lifestyle?
Beyond physical transformation, many followers of the low carb LCHF approach report enhanced mental clarity, emotional stability, and decreased food obsession. By stabilizing blood sugar and insulin levels, LCHF diets often reduce mood swings and brain fog. This improved cognitive function is particularly noticeable during high-focus activities or stressful environments. Moreover, shifting away from the sugar-reward cycle can help break compulsive eating patterns, fostering a healthier psychological relationship with food. Over time, this empowers individuals to make more mindful, consistent choices—free from the peaks and crashes associated with carb dependence.
5. How does a low carb LCHF lifestyle affect gut health and the microbiome?
Contrary to myths that fiber intake plummets on a low carb LCHF lifestyle, many followers consume a wide variety of non-starchy vegetables and fermented foods, which support microbiome diversity. However, abrupt carb restriction without sufficient fiber can lead to temporary digestive issues like constipation. Incorporating prebiotic fibers from sources like chicory root, asparagus, or ground flaxseed can help maintain gut flora. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of a low carb diet high fat diet may benefit those with IBS or leaky gut symptoms. Ultimately, long-term gut health thrives on dietary variety, so rotating fibrous vegetables and natural probiotics is key.
6. Is it possible to follow a low carb diet high fat diet on a tight budget?
While high-quality fats like grass-fed butter and wild-caught fish can be pricey, a low carb diet high fat diet can be surprisingly affordable with smart planning. Eggs, canned sardines, frozen vegetables, and bulk nuts are cost-effective staples. Buying meats in bulk or choosing fattier cuts like chicken thighs or ground beef offers great value and aligns with LCHF macros. Avoiding expensive processed low-carb products also saves money while keeping meals whole-food based. With a little batch cooking and weekly planning, a low carb LCHF lifestyle can be both financially and nutritionally sustainable—even on a limited budget.
7. What are some creative plant-based strategies for following a low carb LCHF lifestyle?
Although LCHF is often associated with meat and dairy, plant-based versions are absolutely possible. Avocados, olives, nuts, seeds, coconut cream, and extra virgin olive oil serve as excellent fat sources. Protein can be obtained through tofu, tempeh, and low-carb plant-based protein powders. Non-starchy vegetables like spinach, cauliflower, and zucchini form the base of many meals. Key considerations include B12 and iron supplementation and monitoring omega-3 intake through algae oil or chia seeds. With creativity and planning, even a vegan low carb LCHF approach can be balanced, nutrient-rich, and aligned with ethical or environmental goals.
8. How does a low carb LCHF lifestyle influence hormonal balance, especially in women?
Hormonal health is deeply impacted by diet, and the low carb LCHF approach can yield both positive and cautionary effects. Many women experience more regular menstrual cycles, reduced PCOS symptoms, and decreased insulin resistance on a low carb diet high fat diet. However, overly restrictive calorie intake or aggressive carb elimination can disrupt thyroid and reproductive hormones. It’s crucial to listen to the body’s cues—fatigue, missed periods, or sleep disruptions may signal the need for recalibration. Incorporating nutrient-dense fats, sufficient protein, and possibly cycling carb intake during different phases of the menstrual cycle can help optimize hormonal resilience.
9. How does the low carb LCHF approach fit into global food cultures and diverse culinary traditions?
One of the most enriching aspects of the low carb LCHF lifestyle is its adaptability across culinary traditions. From Mediterranean olive-oil-based dishes to Korean BBQ, Indian ghee, or Ethiopian stews with clarified butter, many cultures already embrace high-fat, low-carb elements. With minor tweaks—like replacing rice with cauliflower rice or avoiding sugary sauces—most traditional recipes can be made LCHF-compliant. Exploring global cuisines not only prevents dietary boredom but also enhances cultural appreciation and variety. This approach reinforces that the low carb diet high fat diet isn’t about restriction but creative adaptation rooted in both flavor and tradition.
10. What future innovations may shape the low carb LCHF lifestyle in coming years?
Emerging technologies are set to revolutionize the low carb LCHF landscape. Personalized nutrition tools—like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs)—can help users fine-tune their responses to specific foods in real-time. Lab-grown meats and sustainable fats like algae-based oils may offer eco-conscious LCHF solutions. There’s also growing interest in ketone esters and exogenous ketones as performance enhancers and cognitive aids. As clinical research deepens, we’ll likely see more condition-specific LCHF protocols tailored for neurodegenerative diseases, cancer therapy support, and metabolic syndrome. The future of the low carb diet high fat diet lies in precision, sustainability, and broader medical integration.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Low Carb LCHF for Optimal Wellness
In the quest for better health, sharper cognition, and sustainable weight management, the low carb LCHF diet stands out as a transformative and evidence-backed nutritional strategy. Its ability to harmonize protein-rich meals with fat-centric energy metabolism fosters a unique synergy that supports lean muscle, hormonal health, and cognitive clarity. By moving away from outdated, carbohydrate-heavy paradigms and embracing the nuanced benefits of a low carb diet high fat diet, individuals unlock a powerful pathway to better living.
Through consistent, mindful application of low carb LCHF principles, and with careful attention to food quality, nutrient density, and individual needs, this dietary approach offers a credible and flexible foundation for lasting health. Whether you are an athlete, a busy professional, or someone seeking a healthier life trajectory, the science, satisfaction, and sustainability behind the low carb LCHF lifestyle make it a worthy and rewarding path to explore.