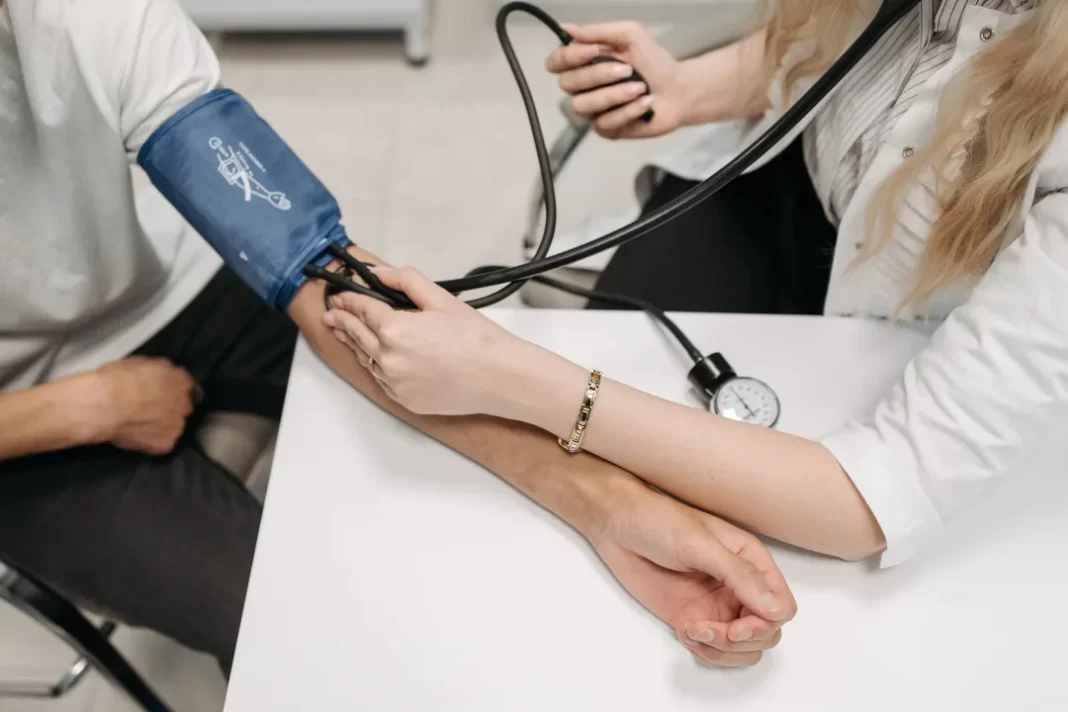
High blood pressure is a serious condition, and medication can be an effective way to treat it. But what are the risks involved with taking these medications? We’ll look at the pros and cons of high blood pressure medication. We’ll also examine its potential side effects and look at some natural supplements that may provide a safer alternative in milder cases of hypertension.
Pros and cons of high blood pressure medication:
High blood pressure defined and its causes
Almost half of the adults in the United States (47%, or 116 million) have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. This chronic medical condition negatively affects the heart and the circulatory system. As blood circulates through the body with increased force, it causes higher-than-normal pressure to build up against the walls of the arteries and, if left untreated, can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other serious health problems. Hypertension is sometimes called the “silent killer” because it can go undetected until a significant cardiac event occurs.
You May Also Like:
The Most Important Supplements for Men Over 40
Dangers Of Benadryl And Melatonin As Sleep Supplements
Per the CDC (Center for Disease Control), “In 2017, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association published new guidelines for hypertension management and defined high hypertension as a blood pressure at or above 130/80 mmHg.”
The causes of high blood pressure are not always clear; many factors may contribute to it, like obesity, lack of exercise, stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, family history, age, and genetics. Lifestyle and dietary contributors such as poor-quality sleep, high salt intake, and not eating enough fruits and vegetables can also play a role.
Understanding the Pros and Cons of High Blood Pressure Medication is an original (HisHealthMag) article.
Pros and cons of high blood pressure medication:
Five commonly prescribed drugs and their side effects.
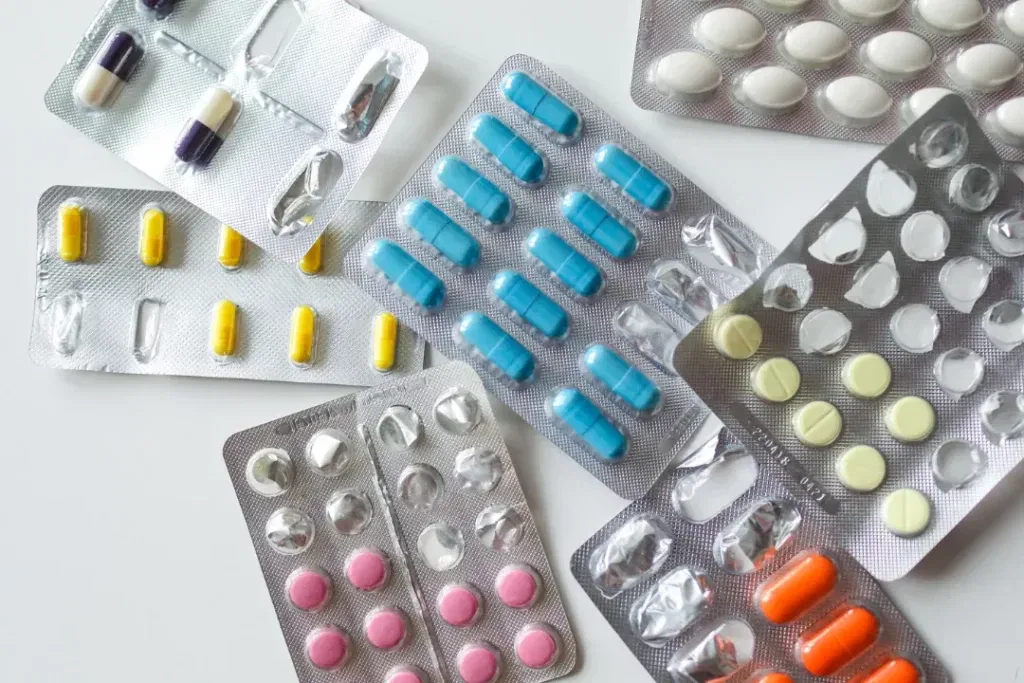
Blood pressure medication (antihypertensive medication) can effectively lower blood pressure; the higher your blood pressure is, the more likely you will benefit from it. People considered high risk for heart attacks and strokes use blood pressure medications to lower high blood pressure and keep their hearts from overworking.
All medications for high blood pressure come with a list of potential side effects, and people can react differently to each drug depending on their medical history, age, and gender. Five commonly used medications for treating high blood pressure are ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, beta-blockers, and angiotensin II receptor blockers. A brief description of how these drugs work and some side effects follow.
1) Diuretics, also known as water pills, work by flushing excess water and salt from your body through urination, reducing the amount of fluid flowing through your veins and arteries, and lowering your blood pressure.
Examples: indapamide and bendroflumethiazide
Possible side effects:
Dizziness (when standing up)
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Rash
Long-term use may lead to low potassium and sodium levels.
2) Beta-blockers are a type of medicine that blocks the action of two natural chemicals in your body: epinephrine and norepinephrine (fight or flight stress reactive hormones). Beta-blockers act on the beta-adrenergic receptors of the sympathetic nervous system, reducing heart rate and force of contraction (cardiac contractility) to lower blood pressure.
Examples: atenolol and bisoprolol
Possible side effects:
Dizziness
Headaches
Tiredness
Cold hands and feet.
3) Calcium channel blockers slow down how your cells use calcium and prevent it from entering heart and artery cells. Since your heart and arteries need calcium to contract, blocking calcium relaxes contraction and widens blood vessels allowing the heart to pump with less force and lowering blood pressure.
Examples: amlodipine, felodipine, nifedipine, diltiazem, and verapamil
Possible side effects:
Headaches
Swollen limbs and ankles
Constipation
Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
4) ACE inhibitors act by blocking angiotensin II (a chemical that causes blood vessels to narrow) and relaxing your veins and arteries to reduce blood pressure. ACE inhibitors are typically prescribed for people with high blood pressure who have not responded well to other treatments, such as diuretics or calcium blockers.
Examples: enalapril, lisinopril, perindopril, and ramipril
Possible side effects:
Persistent dry cough
Headaches
Dizziness
Rash
5) Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) work similarly to ACE inhibitors. They lower blood pressure by protecting blood vessels from angiotensin II, which, to restrict blood vessels, must bind with a receptor site – ARBs stop that from happening to allow for more effortless blood flow resulting in lower blood pressure.
Examples: candesartan, irbesartan, losartan, valsartan, and olmesartan.
Possible side effects:
Dizziness
Headaches
Cold or flu-like symptoms
[This article “Understanding the Pros and Cons of High Blood Pressure Medication” is originally published on HisHealthMag]
After considering the pros and cons of high blood pressure medication, what’s the alternative?
In less severe cases of hypertension, natural supplements, such as herbs and minerals, can help lower blood pressure without the harsh side effects of prescription medications. If your doctor determines that you are not at “high risk” for a major cardiac event, natural supplements that can reduce blood pressure may be an option for you.
Let’s look at three of the most effective natural supplements to lower your blood pressure: hawthorn, rosella, and ginger.
Hawthorne is a plant in the rose family that has been used as far back as the 1st century BCE for its medicinal properties, especially for heart health. It’s known for reducing high blood pressure, increasing circulation, improving muscle function, and decreasing inflammation.
Procyanidins (a type of polyphenol) in Hawthorn work as a natural ACE inhibitor, relaxing arteries and widening blood vessels easing the job of your heart during contractions and increasing the amount of blood pumped out of the heart.
Hawthorn is also associated with brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD) improvements.
FMD is an indirect measurement of how much nitric oxide is released by your body, and nitric oxide is essential in relaxing your veins and arteries to lower blood pressure.
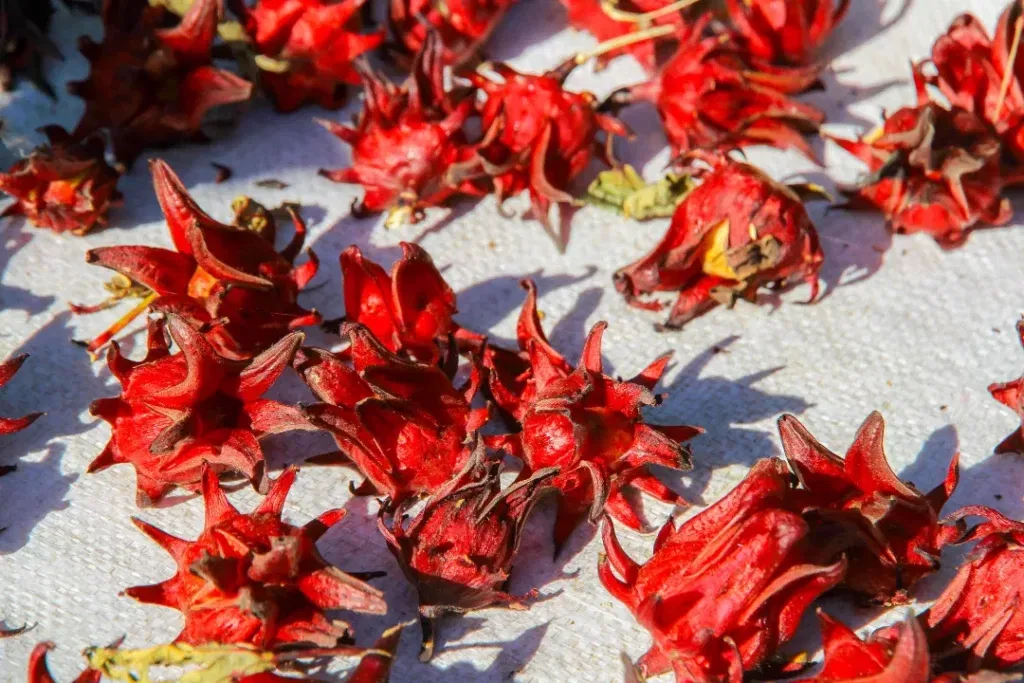
Rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa) is a plant in the citrus family containing anthocyanins (plant pigments) shown to lower blood pressure. A control study revealed that subjects who drank hibiscus tea daily significantly reduced their blood pressure; in fact, the tea was more effective than the medication Captopril. Another study posted online in 2020 also concluded that rosella decreased high blood pressure.
Ginger is a spice and a plant native to Asia that has been used for centuries for heart health.
Today it is cultivated worldwide for its culinary and medicinal use.
Human and animal studies show ginger can lower blood pressure by working as a
natural calcium channel blocker and ACE inhibitor, relaxing and widening blood vessels and requiring less effort for your heart to pump blood. This study of more than 4,000 people showed that those who consumed ginger had the least risk of high blood pressure.

Pros and cons of high blood pressure medication:
Some safe, natural supplements that reduce blood pressure.
An internet search will pull up dozens of supplements that reduce blood pressure which can be purchased individually, but one of the most efficient and effective ways to take them is as blends. For example, Medicine Man Plant Co. has combined the three potent supplements mentioned in this article in capsule form, aptly named the Blood Pressure Pill. Medicine man believes that “multiple action: as proven time and again, diversity brings strength. By harnessing the different properties of several plants, more complete support of the heart and cleaning of the circulatory system is obtained.”
Medicine Man Co. has multiple scientific studies on their website proving the effectiveness of these ingredients in lowering and maintaining healthy blood pressure. All their products are responsibly sourced and harvested, non-GMO, 3rd Party tested, and manufactured in the US at state-of-the-art cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practice) facilities.

Understanding the Pros and Cons of High Blood Pressure Medication is the (HisHealthMag) report.
Understanding the pros and cons of high blood pressure medication:
Concluding thoughts.
While prescription blood pressure medications are effective, unless your doctor says you’re a “high risk” case, you might want to avoid taking them because of their potential side effects. If your hypertension is mild, natural supplementation could be a safe first step in meeting your blood pressure goals; combined with some lifestyle changes, you may not need prescription drugs. Staying in touch with your doctor and monitoring your blood pressure will show you if the supplements are working.
Whether you use natural supplements or take prescription medications, consider adding non-medicinal treatments such as losing weight, reducing alcohol and sodium intake, increasing physical activity, and quitting smoking to bring blood pressure numbers down and maintain those good numbers for life.
For your further reference:
Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) | UCSF Health
Facts About Hypertension | cdc.gov
Types of Blood Pressure Medications | American Heart Association
10 ways to control high blood pressure without medication – Mayo Clinic
When is taking medication for high blood pressure a good idea? – InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf
Blood pressure-lowering supplements: 5 of the best options
Important Note: The information contained in this article (Understanding the Pros and Cons of High Blood Pressure Medication) is for general informational purposes only, and should not be construed as health or medical advice, nor is it intended to diagnose, prevent, treat, or cure any disease or health condition. Before embarking on any diet, fitness regimen, or program of nutritional supplementation, it is advisable to consult your healthcare professional in order to determine its safety and probable efficacy in terms of your individual state of health.
Regarding Nutritional Supplements Or Other Non-Prescription Health Products: If any nutritional supplements or other non-prescription health products are mentioned in the foregoing article, any claims or statements made about them have not been evaluated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and such nutritional supplements or other health products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.