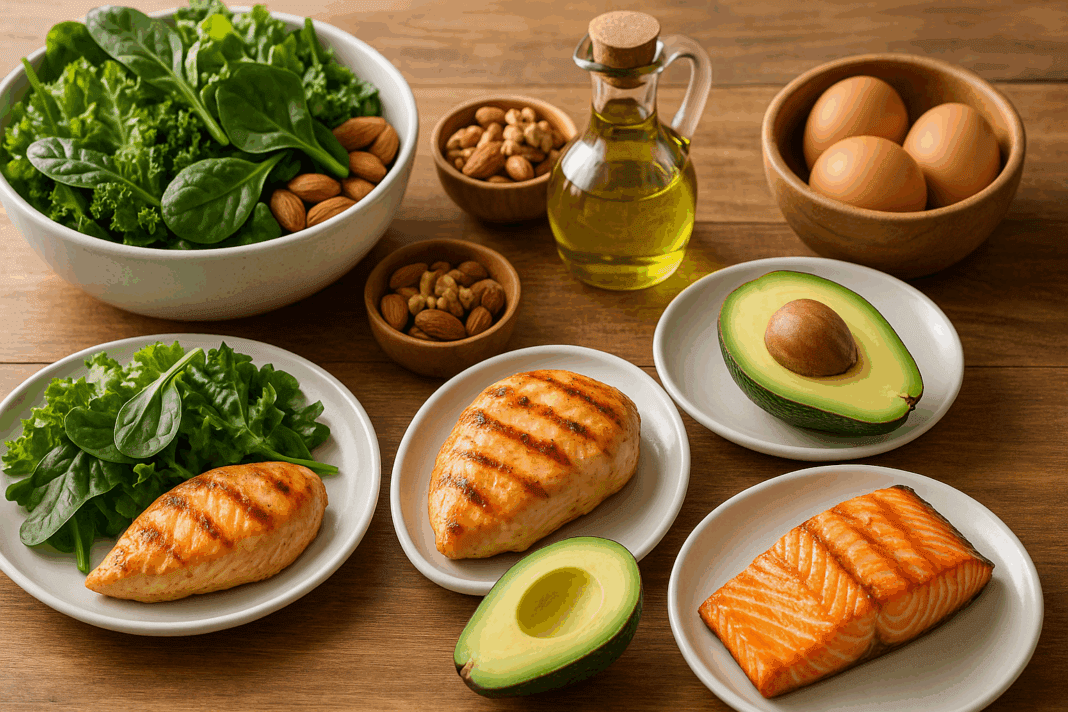
Achieving lasting nutritional success often requires a shift in how we approach our daily meals. For those seeking to enhance their health, boost their energy, or lose fat while preserving lean muscle mass, a high protein low carb diet meal plan can serve as a transformative strategy. This dietary model has surged in popularity not only for its physiological benefits but also for its adaptability to diverse lifestyles. Whether your goal is weight loss, metabolic efficiency, or muscle gain, understanding how to properly implement and sustain a high protein low carb diet plan is essential.
You may also like : The Ultimate Guide to Choosing a High Protein Diet Name That Fits Your Goals
Understanding the Science Behind High Protein Low Carb Nutrition
To appreciate the full benefits of this approach, it is important to examine the scientific rationale that supports it. Protein plays a fundamental role in the human body by supporting muscle repair, enzymatic function, hormone production, and immune system efficiency. Meanwhile, carbohydrates, though not inherently detrimental, can lead to energy crashes, weight gain, or insulin resistance when consumed in excess, particularly from refined sources. By prioritizing protein intake and reducing carbohydrate consumption, the body is nudged toward utilizing fat as its primary energy source, a state known as ketosis in more extreme applications like the ketogenic diet.
Research consistently shows that a high protein intake can enhance satiety, leading to reduced caloric intake throughout the day. Moreover, protein requires more energy to metabolize compared to fats or carbs, a phenomenon known as the thermic effect of food. This means your body burns more calories simply by digesting protein-rich meals. Combining these benefits with lowered carb intake fosters improved insulin sensitivity, reduced blood sugar spikes, and more stable energy levels throughout the day.
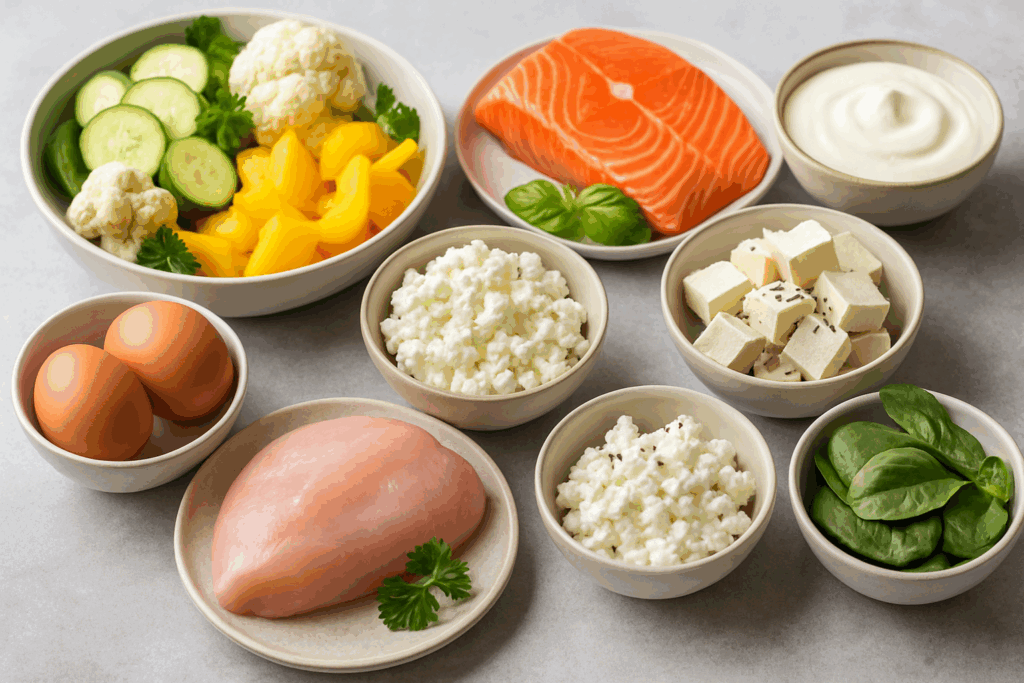

What to Eat on a High Protein Low Carb Diet
Creating a sustainable high protein low carb diet meal plan starts with selecting the right foods. Protein sources should be high-quality and diverse. This includes lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and pork loin, as well as fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, which also offer heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Plant-based protein sources, such as tofu, tempeh, and legumes, can be incorporated in moderation depending on carb tolerance.
Dairy products like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and hard cheeses are excellent options, provided they are unsweetened and minimally processed. Eggs, a nutrient-dense powerhouse, offer versatility in meal preparation and are highly bioavailable. For low-carb vegetables, leafy greens, zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, bell peppers, and asparagus should make up the bulk of your plate, delivering fiber, vitamins, and minerals without a carbohydrate overload.
Healthy fats play a supporting role in a high protein low carb diet. Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and coconut oil not only add flavor and satiety but also help maintain hormonal balance and cellular function. Whole foods should always be prioritized over packaged diet products to minimize hidden sugars and additives.
How Much Protein on a Low Carb Diet?
Determining how much protein on a low carb diet is appropriate depends on individual goals, activity levels, and body composition. For most individuals, a daily protein intake ranging from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight is sufficient to support muscle maintenance and metabolic function. Athletes or those engaged in regular resistance training may benefit from the higher end of this spectrum.
Balancing macronutrients effectively is key. For example, a person weighing 70 kilograms may aim for 84 to 140 grams of protein per day. This should be spaced evenly across meals to optimize absorption and muscle protein synthesis. Importantly, while low carb does not necessarily mean no carb, total daily carbohydrate intake typically ranges from 20 to 100 grams depending on personal tolerance and whether the goal is general health, fat loss, or therapeutic ketosis.
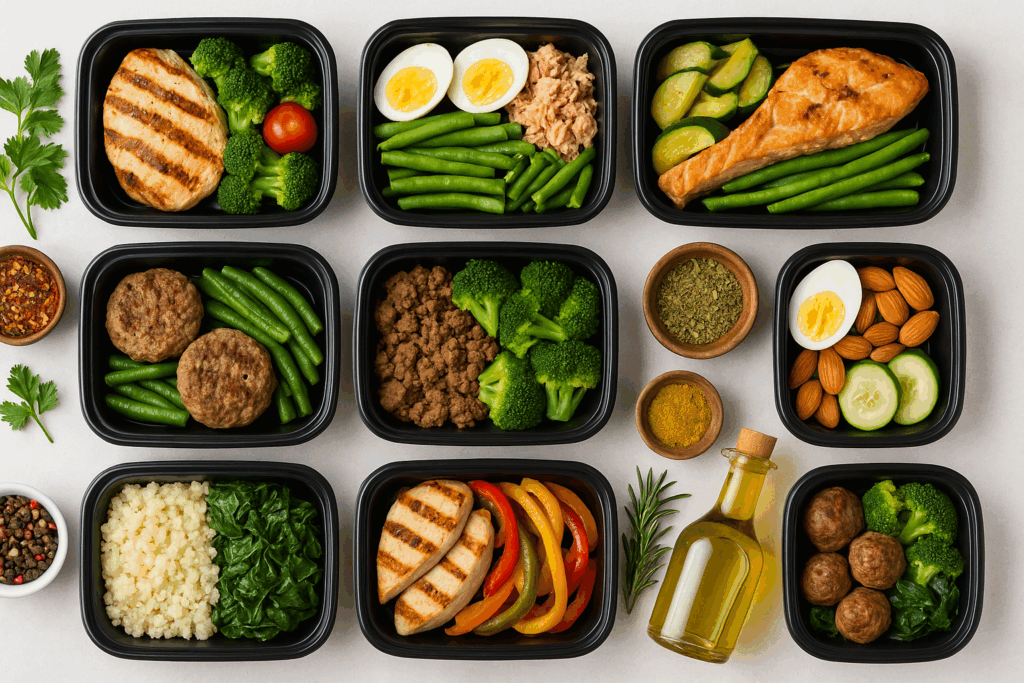

Structuring a High Protein Low Carb Diet Meal Plan
A structured meal plan can help eliminate guesswork and maintain consistency. Begin your day with a protein-packed breakfast, such as scrambled eggs with spinach and feta, or a Greek yogurt parfait with chia seeds and almonds. Mid-morning snacks could include a hard-boiled egg or slices of turkey wrapped around avocado.
Lunch might consist of grilled chicken breast atop a bed of mixed greens, drizzled with olive oil and lemon juice. A low carb high protein snack later in the day might involve cottage cheese with cucumber slices or a protein shake with unsweetened almond milk. For dinner, options like seared salmon with roasted cauliflower or a steak with steamed broccoli and butter provide flavor and nutrition without excess carbs.
A weekly high protein low carb meal plan should include variety to prevent boredom and ensure a wide range of nutrients. Rotate protein sources, switch up vegetables, and experiment with herbs and spices to keep meals exciting. Meal prepping on weekends can save time and make adherence easier during busy weekdays.
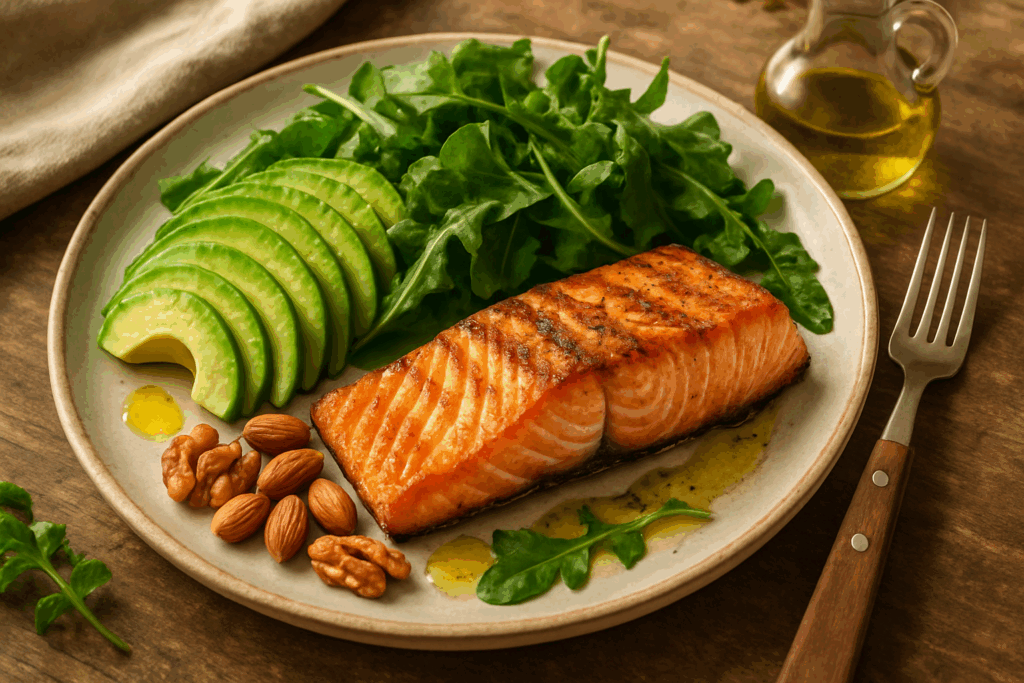

Benefits of a High Protein Low Carb High Fat Approach
One variant of this dietary strategy is the high protein low carb high fat model, which provides ample energy through healthy fats while minimizing insulin secretion. This combination can support mental clarity, reduced cravings, and sustained satiety. Unlike traditional low-fat diets that may leave individuals feeling hungry or deprived, this approach emphasizes nutrient density and satisfaction.
The inclusion of dietary fats does not automatically equate to weight gain. In fact, fats like those found in nuts, seeds, oily fish, and avocados can enhance fat metabolism and hormone production. They also allow for more flexible meal planning, as fat adds richness and flavor that can be lacking in other restrictive diets. It is important, however, to differentiate between healthy fats and processed trans fats found in fried or packaged foods, which should be strictly avoided.
Navigating Challenges and Side Effects of High Protein Low Carb Diets
While the benefits of a high protein low carb diet are significant, it is not without challenges. One common concern is the initial adaptation phase, where some individuals may experience fatigue, irritability, or digestive changes as the body shifts from carb dependence to fat metabolism. Staying well-hydrated, increasing sodium and potassium intake, and gradually tapering carbs can mitigate these effects.
Another concern involves the side effects of high protein low carb diet plans on kidney health. While this diet is generally safe for healthy individuals, those with preexisting kidney conditions should consult a healthcare provider before dramatically increasing protein intake. Long-term adherence may also pose risks if the diet is overly restrictive or lacks diversity.
To maintain balance, ensure the inclusion of fiber-rich vegetables and sufficient hydration to support digestion and overall metabolic health. Additionally, listening to hunger cues and avoiding overconsumption of protein is essential. Excessive protein beyond what the body requires is not stored as muscle but can be converted to glucose, which may interfere with fat loss goals in some individuals.
High Protein Low Carb Diet Foods to Keep on Hand
Stocking your pantry and refrigerator with the right ingredients is fundamental to success. High protein low carb diet foods such as eggs, canned tuna, frozen spinach, and protein powder offer convenience and versatility. Nuts and seeds provide portable snacks, while full-fat yogurt and cheese deliver calcium and probiotics without excess sugar.
Lean meats, poultry, and fish should be staples, with frozen options allowing for longer storage. Low-carb vegetables like zucchini, mushrooms, and cabbage can be used in soups, stir-fries, or roasted as side dishes. For sweet cravings, options like stevia or erythritol can replace sugar in recipes without affecting blood sugar levels.
Creating a shopping list focused on whole, unprocessed foods not only ensures better nutrition but also prevents impulsive purchases of carb-laden snacks. Planning meals in advance and keeping quick-prep ingredients on hand can make the difference between success and regression.
What Does a High Protein Low Carb Diet Look Like in Practice?
In daily practice, a high protein low carb diet plan emphasizes protein-centric meals paired with non-starchy vegetables and healthy fats. For example, breakfast may feature a three-egg omelet with mushrooms and Swiss cheese. Lunch could be grilled shrimp over arugula with avocado slices, while dinner might involve roasted turkey breast with green beans and olive oil.
Between meals, a snack of celery sticks with almond butter or beef jerky without added sugar fits within the plan. Beverages should consist of water, herbal teas, or black coffee to minimize unnecessary calories. The key is simplicity, consistency, and an ongoing commitment to nutrient-rich choices that align with individual health goals.
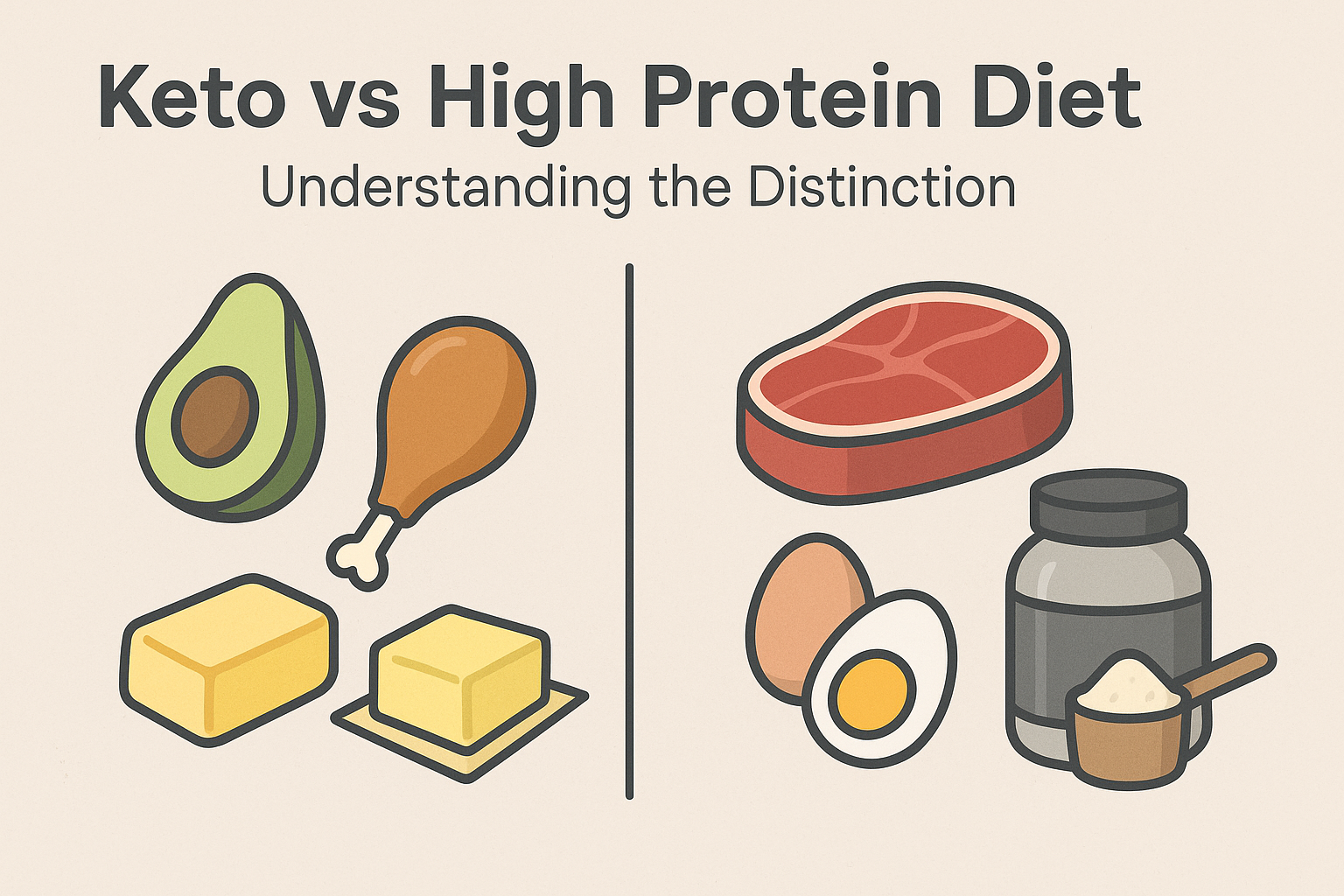
Keto vs High Protein Diet: Understanding the Distinction
It is important to distinguish between a high protein low carb meal plan and the ketogenic diet. While both limit carbohydrate intake, keto emphasizes high fat and moderate protein, with the primary goal of entering and maintaining nutritional ketosis. By contrast, high protein low carb diets typically prioritize protein for muscle maintenance and satiety, with fat intake varying according to personal preferences.
This distinction matters for those with specific goals. For instance, bodybuilders may lean toward high protein to preserve lean mass during fat loss, while individuals managing epilepsy or insulin resistance might benefit more from a strict ketogenic regimen. Understanding the nuances between these two strategies allows for better customization and more effective outcomes.
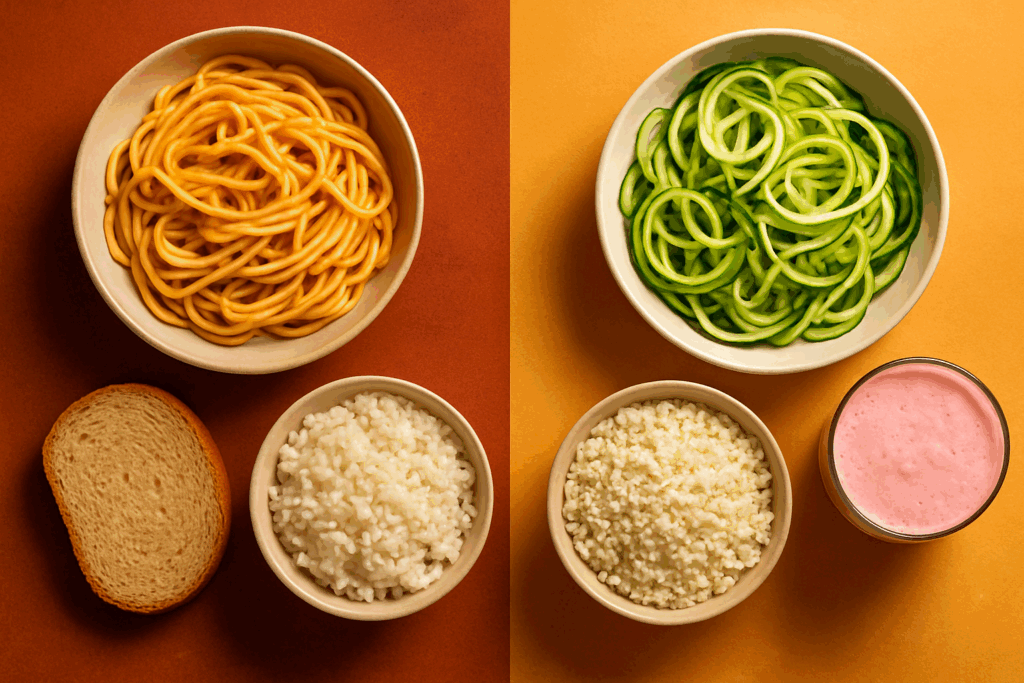

How to Eat More Protein and Less Carbs Without Compromise
Making the shift to a less carbs more protein diet doesn’t have to feel restrictive. Begin by gradually reducing starchy carbs like bread, pasta, and rice, replacing them with vegetable-based alternatives such as cauliflower rice or spiralized zucchini. Use herbs, spices, and healthy fats to enhance flavor and avoid the monotony that can derail progress.
Incorporate protein into every meal and snack. For instance, add a scoop of protein powder to smoothies, top salads with grilled chicken, or snack on cheese sticks and nuts. Choose meals that naturally prioritize protein and have carb-conscious sides. Maintaining variety, flavor, and flexibility ensures long-term adherence and enjoyment.
Adapting for Special Populations: Seniors, Children, and Pregnant Women
A high protein low carb nutrition plan can be adapted to various life stages with appropriate modifications. For seniors, protein is essential to combat sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss). Pairing adequate protein with resistance training can maintain strength, mobility, and independence. Low carb strategies also support blood sugar regulation, which is particularly beneficial for aging adults at risk for type 2 diabetes.
For children, the emphasis should remain on whole foods and balanced meals. While extreme low carb diets are generally discouraged for growing bodies, emphasizing protein and limiting added sugars can foster lifelong healthy habits. Pregnant women should approach low carb eating with caution, focusing on nutrient density and ensuring adequate intake of folate, iron, and calcium. Moderate carb restriction, rather than strict elimination, often works best in these cases.
Meal Timing and Intermittent Fasting Synergies
Combining a high protein low carb diet with intermittent fasting (IF) can amplify health benefits. IF involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting, with popular protocols including 16:8 (16 hours fasting, 8 hours eating) or alternate-day fasting. When aligned with a protein-rich, low carb intake, IF can accelerate fat loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and support autophagy.
Protein is particularly advantageous during feeding windows because it helps preserve lean muscle mass, which is a risk during extended fasting periods. Many people find that high protein meals help them feel satiated longer, making fasting windows easier to manage. As with any dietary intervention, IF should be approached gradually and monitored for individual tolerance.
Mental Health and Cognitive Function on a High Protein Low Carb Meal Plan
Nutrition profoundly impacts mental health, and a high protein low carb diet has been linked to cognitive benefits such as improved focus, memory, and mood stability. Protein provides the building blocks for neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. A diet rich in tryptophan (found in turkey, eggs, and dairy) and tyrosine (found in chicken, beef, and legumes) supports emotional regulation and cognitive performance.
Moreover, reducing carbohydrate intake—particularly refined sugars—can stabilize blood sugar levels, which in turn reduces mood swings and anxiety. Emerging research on the gut-brain axis also highlights how dietary changes impact mental well-being. With a diverse, whole-foods-based low carb high protein menu plan, individuals often report reduced brain fog, better sleep, and enhanced productivity.
Customizing a Low Carbohydrate High Protein Diet Plan for Your Goals
One of the greatest strengths of a low carbohydrate high protein diet plan is its adaptability. Whether you’re focused on weight loss, muscle gain, or blood sugar control, the macronutrient ratios can be tailored to meet your objectives. For fat loss, a moderate calorie deficit with high protein helps preserve lean mass. For muscle building, pairing increased protein with strategic carb timing around workouts can enhance recovery.
Tracking food intake using apps or journals can improve accountability and identify nutrient gaps. Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist ensures the plan is balanced and sustainable. Remember, no one-size-fits-all approach exists, and individual preferences, tolerances, and goals should drive dietary decisions.
Supplements That Complement a High Protein Low Carb Lifestyle
Though whole foods are the foundation of any healthy diet, certain supplements can support a high protein low carb approach. Whey or plant-based protein powders are convenient for meeting daily protein goals, especially post-workout or during busy mornings. Creatine monohydrate supports strength and cognitive function, making it ideal for active individuals.
Magnesium, potassium, and sodium are key electrolytes that can be depleted on a low carb plan. Supplementing or consuming mineral-rich foods like spinach, avocados, and bone broth can prevent fatigue and muscle cramps. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil support heart and brain health, especially when dietary sources are limited. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
Overcoming Social and Emotional Challenges
Adopting a high protein low carb diet can be socially and emotionally challenging, particularly in cultures where bread, pasta, and desserts are staples. Navigating holidays, social gatherings, and peer pressure requires planning and confidence. Bringing your own dishes to potlucks, choosing protein-based appetizers, or eating beforehand can help you stay on track without feeling deprived.
Emotional eating is another obstacle. High protein foods like turkey, tuna, and eggs can help manage cravings, but developing non-food coping strategies such as mindfulness, exercise, or journaling can provide emotional support. Having a strong “why” behind your dietary changes strengthens resilience when faced with temptation.
Long-Term Sustainability: Periodization and Flexibility
Sustainability is perhaps the most critical component of any nutrition plan. While some thrive on a strict high protein low carb regimen indefinitely, others benefit from periodization, where phases of low carb eating alternate with phases of increased carbs or calories. This can prevent adaptation, improve metabolic flexibility, and support mental well-being.
Flexibility does not mean abandoning core principles but rather learning how to adapt the plan to life’s inevitable changes. Travel, illness, stress, or special events may require adjustments. Having a foundation of protein-rich, nutrient-dense habits allows you to return to your plan without guilt or disruption.
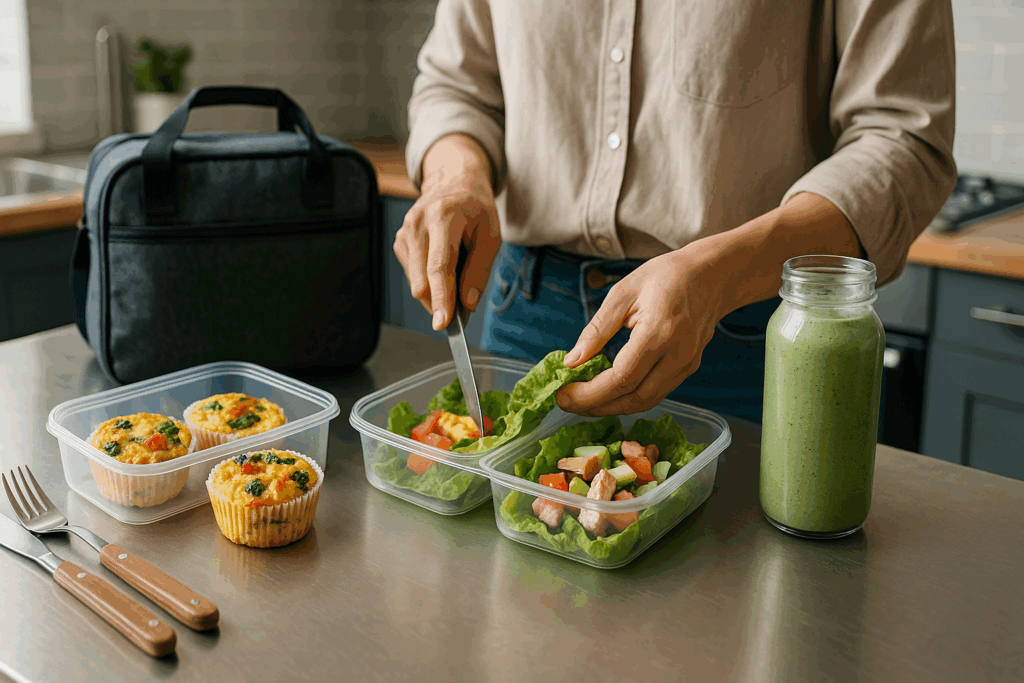

Exploring Low Carb High Protein Menu Plans for Busy Lifestyles
Busy schedules shouldn’t be a barrier to healthy eating. A low carb high protein menu plan can be structured to accommodate even the most hectic days. Quick breakfasts like protein shakes, egg muffins, or low-carb smoothies can be prepared in advance. Lunches such as grilled meat wraps in lettuce leaves or meal-prepped salads with tuna offer convenience without compromising nutrition.
For dinner, slow cooker recipes or sheet pan meals minimize cleanup and save time. Think of dishes like chicken thighs with Brussels sprouts or beef stir-fry with bok choy. Even dining out is possible with careful choices—opt for grilled proteins, steamed vegetables, and ask for sauces on the side. Preparation and awareness are the cornerstones of success when time is limited.
Cultural Variations of High Protein Low Carb Diets
Around the world, traditional diets often align more closely with high protein low carb principles than modern Western diets. For example, the Inuit traditionally consumed a diet rich in marine protein and fat with negligible carbohydrates. Similarly, certain African and Middle Eastern diets center on goat meat, fish, eggs, and leafy greens. Exploring these cultural variations can help individuals personalize their high protein low carb meal plan while avoiding dietary monotony.
Japanese cuisine offers sashimi, miso soup, and seaweed, all of which are low in carbs and high in beneficial nutrients. Mediterranean diets can be adapted by emphasizing grilled meats, olives, feta, and non-starchy vegetables while minimizing bread and pasta. Even Latin American diets can be tweaked by focusing on meats, avocados, and leafy greens while reducing rice and tortillas. Respecting cultural food traditions adds emotional satisfaction and increases the likelihood of long-term adherence.
What Foods Have High Protein and Low Carbs? Exploring Smart Choices
A wide variety of high protein low carb foods exist to satisfy different tastes and preferences. Meats, poultry, and seafood are obvious choices, but don’t overlook eggs, which deliver essential amino acids in a compact package. Dairy items like hard cheeses and strained yogurts also provide protein with minimal carbs.
For plant-based eaters, soy products, seitan, and select legumes offer protein, though careful portion control is essential due to the higher carb content. Creative recipes such as cauliflower crust pizza, zucchini lasagna, or eggplant parmesan can mimic traditional comfort foods while aligning with a high protein low carb diet plan. Smart food selection transforms your kitchen into a hub of nutritious possibilities.
The Future of High Protein Low Carb Diets in Public Health
As chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular illness continue to rise, the relevance of high protein low carb diets in public health becomes increasingly significant. Governments and institutions are beginning to recognize the role of refined carbohydrates and sugar in driving metabolic disease. Programs that educate communities on the benefits of reducing carbs and increasing protein could play a crucial role in reversing these trends.
Furthermore, advances in personalized nutrition, such as genetic testing and microbiome analysis, will allow individuals to fine-tune their macronutrient needs more precisely. As data accumulates, future dietary guidelines may shift to reflect the benefits of a high protein low carb framework, especially when integrated with exercise, sleep, and stress management.
Frequently Asked Questions: Advanced Insights into the High Protein Low Carb Diet Meal Plan
1. How can I use a high protein low carb diet meal plan to support long-term metabolic flexibility?
Metabolic flexibility refers to the body’s ability to efficiently switch between burning carbohydrates and fat for fuel depending on availability. A high protein low carb diet meal plan encourages the body to rely more on fat metabolism, but it also primes it for improved adaptation over time. To support metabolic flexibility, consider incorporating occasional refeed days where healthy complex carbohydrates are reintroduced in moderation, especially after intense workouts. This strategy can help prevent hormonal stagnation, boost thyroid function, and improve athletic performance without reversing your progress. Over time, this metabolic adaptation reduces dependence on constant carbohydrate intake and supports better energy balance and cognitive clarity in varied scenarios.
2. What foods have high protein and low carbs but are also minimally processed and eco-conscious?
For those who prioritize clean eating and sustainability, choosing high protein low carb diet foods with minimal processing is essential. Options include pasture-raised eggs, wild-caught sardines, grass-fed beef liver, and sustainably sourced bison. These choices are rich in micronutrients like B12, iron, and zinc while maintaining a favorable protein-to-carb ratio. Incorporating seasonal vegetables like Swiss chard or mustard greens ensures a low glycemic load and enhances the diet’s fiber content. If you’re environmentally conscious, consider plant-based high protein low carb foods such as fermented tempeh or spirulina, which offer impressive protein density with low ecological impact.
3. Is high protein low carb good for weight loss when combined with resistance training?
Yes, the synergy between a high protein low carb diet plan and resistance training is particularly potent for sustainable fat loss and lean muscle retention. Resistance training amplifies the need for amino acids, and the high protein content in this plan ensures muscle repair and growth while keeping insulin levels stable. Reducing carb intake, especially from refined sources, minimizes water retention and bloating, offering quicker visible changes in body composition. Over time, this combination promotes metabolic efficiency by increasing muscle mass, which boosts resting energy expenditure. To maximize results, time your protein intake post-workout and consider carb cycling to optimize glycogen replenishment without compromising fat loss goals.
4. How to eat more protein and less carbs without falling into repetitive meal routines?
Avoiding mealtime monotony while following a less carbs more protein diet is achievable with creativity and strategic planning. Consider rotating animal-based proteins like duck, lamb, or venison alongside seafood options such as octopus or scallops. For breakfast, swap traditional eggs with high protein no carb foods like smoked salmon or turkey sausage, paired with sautéed spinach or avocado. Use global cuisines to diversify your meals—Middle Eastern grilled kebabs, Japanese sashimi platters, or Mediterranean eggplant rolls stuffed with herbed ricotta all fit within a high protein low carb meal plan. Additionally, try meal theme nights (like “Tex-Mex Tuesday” or “Keto Curry Night”) to spark variety without deviating from your goals.
5. What are the lesser-known side effects of high protein low carb diet plans, and how can they be managed?
While many focus on immediate benefits, it’s important to understand and manage the subtle side effects of high protein low carb diet plans. One overlooked issue is the potential decline in serotonin levels, especially if carbs are restricted too drastically. This can affect mood and sleep, as carbohydrates play a role in tryptophan transport to the brain. To counter this, incorporate slow-digesting carbs from vegetables like butternut squash or use adaptogens such as ashwagandha to balance cortisol levels. Another potential issue is digestive sluggishness due to reduced fiber intake; counter this with high protein low fat low carb foods that are also rich in fiber, like chia seeds and artichokes. Always ensure hydration and adequate electrolyte intake to mitigate fatigue or cramping.
6. What does a high protein low carb diet look like in climates or cultures with limited animal protein access?
In regions where animal protein is scarce or culturally limited, a low carbohydrate high protein diet plan can still be successfully implemented using regional ingredients. Legumes such as black soybeans or lupini beans are higher in protein and lower in net carbs compared to conventional beans. In Southeast Asia, high protein low carb diet foods include tempeh, fermented fish, and duck eggs, while in India, paneer and spiced lentil flours like besan (in moderation) can support protein intake. In colder climates, smoked fish, dairy, and preserved meats form the backbone of a sustainable high protein diet and low carbs plan. It’s about adjusting the sources to match local availability while maintaining macronutrient goals.
7. How do low carb high calorie foods fit into a high protein low carb diet plan for bulking?
For individuals aiming to build muscle or gain weight on a low carb nutrition plan, incorporating low carb high calorie foods is essential to meet energy needs. Foods like macadamia nuts, ghee, coconut cream, and fatty cuts of lamb provide dense calories without increasing carbohydrate intake. Pair these with high protein low carb high fat dishes such as chicken thighs cooked in avocado oil or salmon patties topped with aioli. To support anabolic processes, timing meals around resistance training and including multiple feedings throughout the day is key. A low carb high protein menu plan designed for bulking should prioritize caloric density without relying on processed or sugary foods.
8. What are some emerging technologies or tools that support a high protein low carb lifestyle?
Digital tools and innovations have made it easier than ever to adhere to a high protein low carb diet meal plan. Apps like Carb Manager and Cronometer provide advanced nutrient tracking that includes amino acid breakdowns and net carb calculations. Smart kitchen devices such as air fryers and sous-vide machines allow for high-quality protein preparation without added oils or breading. Wearable metabolic trackers, like Lumen or CGMs (continuous glucose monitors), offer real-time biofeedback on how foods affect your glucose levels and fat-burning status. Meal delivery services now offer customizable high protein low fat low carb meals tailored to specific goals, making consistency easier even during busy periods.
9. How can someone integrate a high protein low carb diet into low carb diet programs for families?
Integrating a high protein low carb diet into family-focused low carb diet programs requires flexibility and creativity. One approach is to create a meal base that satisfies all family members—for example, taco night with ground beef, lettuce wraps for adults, and whole grain tortillas for children. Another is to batch-cook proteins such as grilled chicken or turkey meatballs and then allow each family member to customize their plate with various sides. Kids may benefit from the inclusion of slow-release carbs like sweet potatoes, while adults stick to high protein low carb diet meal plan principles. Cooking together and involving children in food prep fosters healthy habits and ensures everyone enjoys the meals.
10. What to eat on a high protein low carb diet while traveling or dining out?
Maintaining your high protein low carb diet plan while traveling requires strategic thinking but is entirely feasible. Opt for grilled or roasted meats, bun-less burgers, omelets, or seafood dishes in restaurants. Bring portable high protein no carb foods such as beef jerky, hard-boiled eggs, or pre-portioned nuts to avoid carb-heavy snacks. Airports increasingly offer low carb protein options like cheese trays or salads with grilled chicken. Look for low carb low sugar diet plan items on menus, such as Caesar salads without croutons or steak and steamed greens. Planning ahead, reviewing menus online, and requesting substitutions can help you stay aligned with your dietary goals without compromising enjoyment.
Conclusion : Sustaining the High Protein Low Carb Lifestyle
Embracing a high protein low carb diet meal plan is more than a temporary fix—it is a long-term lifestyle strategy that offers lasting benefits. From improved body composition and metabolic health to enhanced energy and reduced cravings, the rewards are substantial when the plan is personalized and sustainably implemented. The key lies in consistency, variety, and mindfulness.
Take time to reflect on what works for you. Continue exploring new recipes, stay informed about nutritional science, and adjust your approach as your body and goals evolve. The journey to optimal health is ongoing, but with the right tools, information, and dedication, a high protein low carb approach can be both effective and deeply rewarding.
Further Reading:
12 high-protein low-carb meals
7-Day High-Protein Low-Carb Meal Plan, Created by a Dietitian